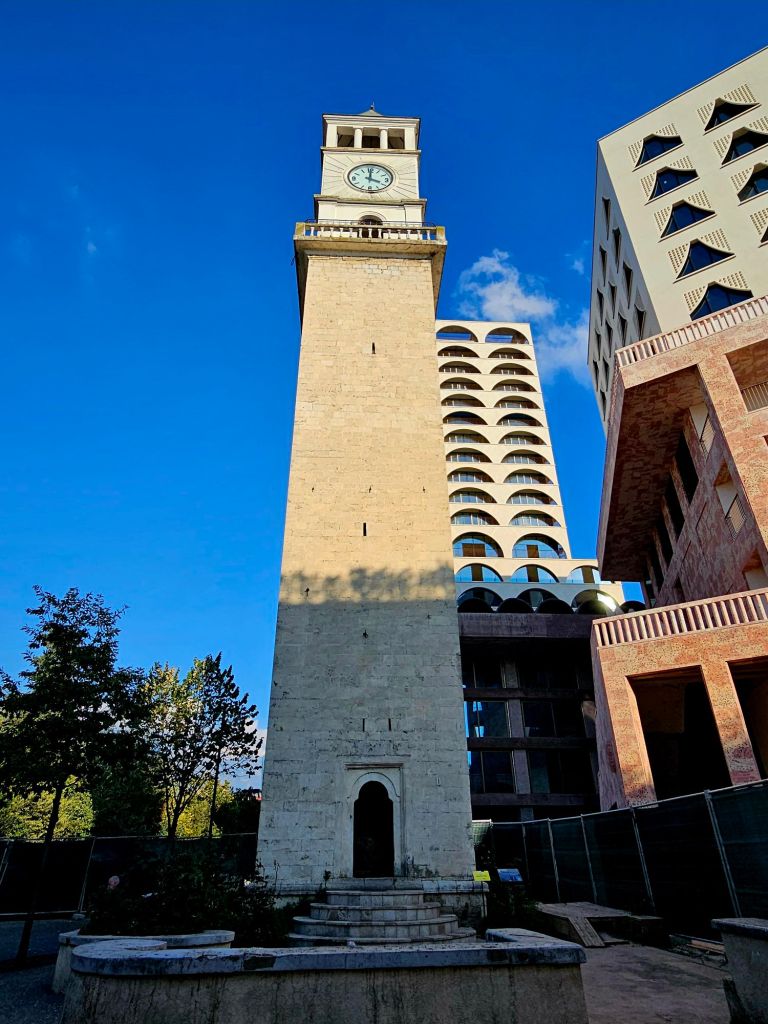
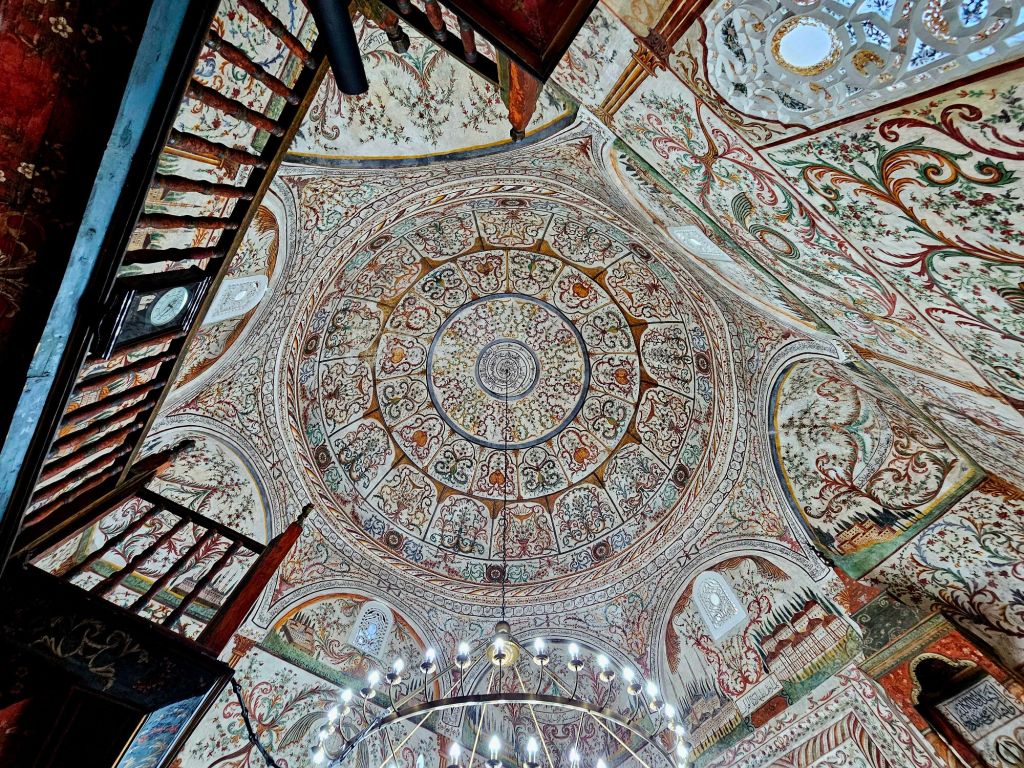
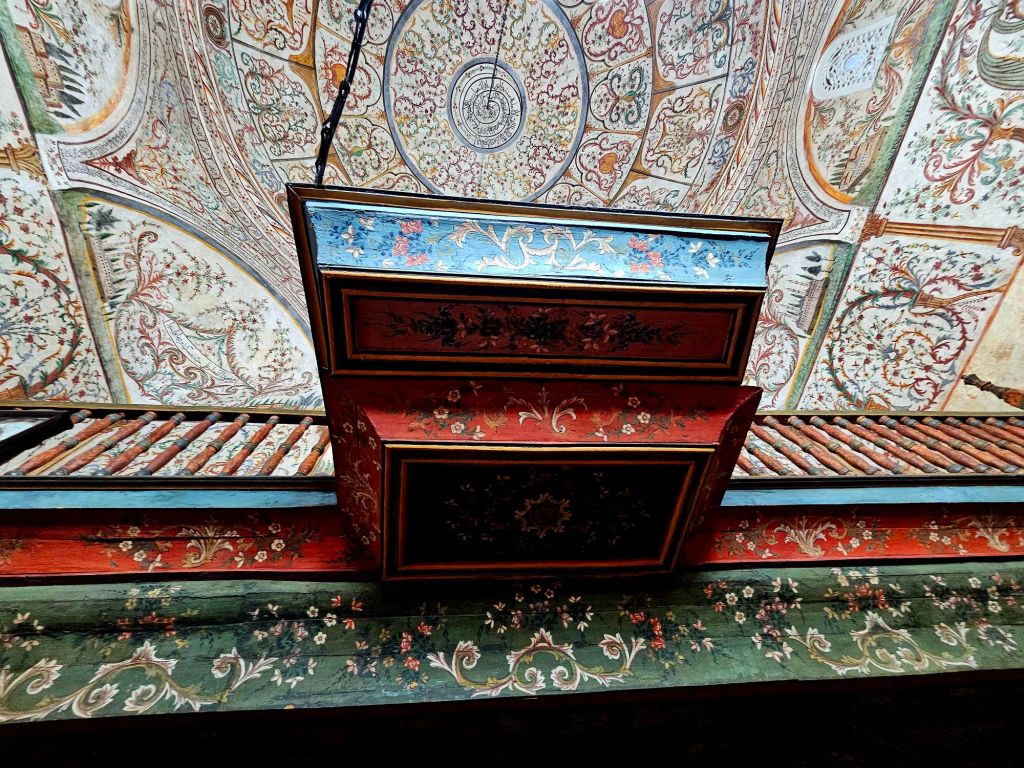
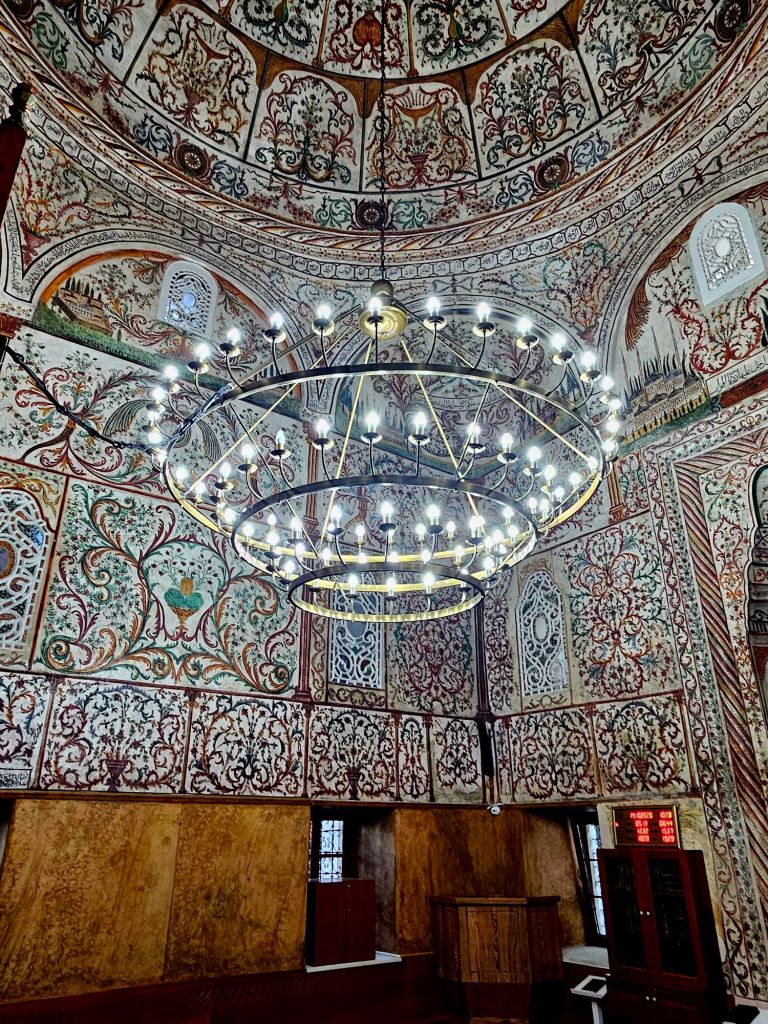
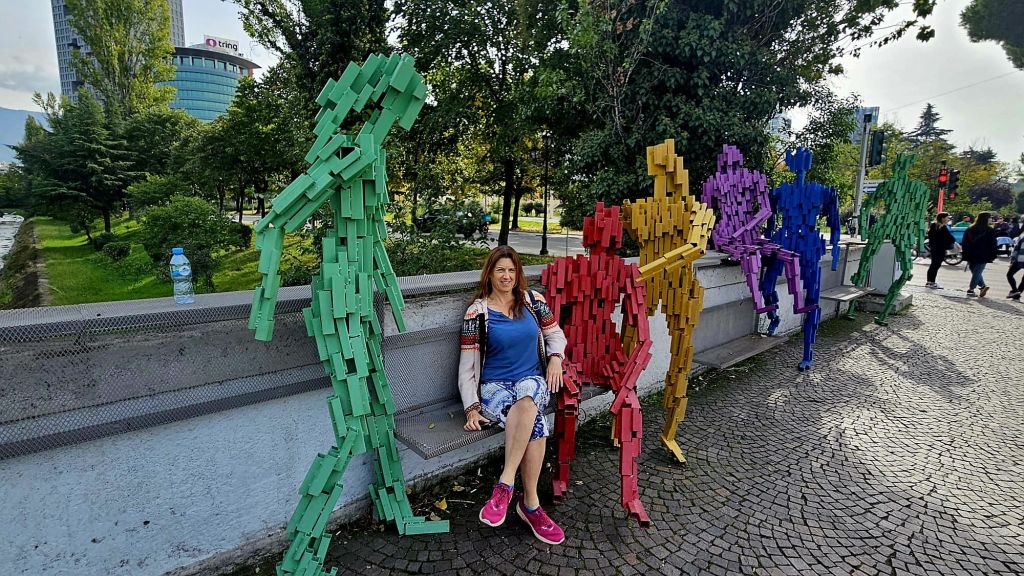
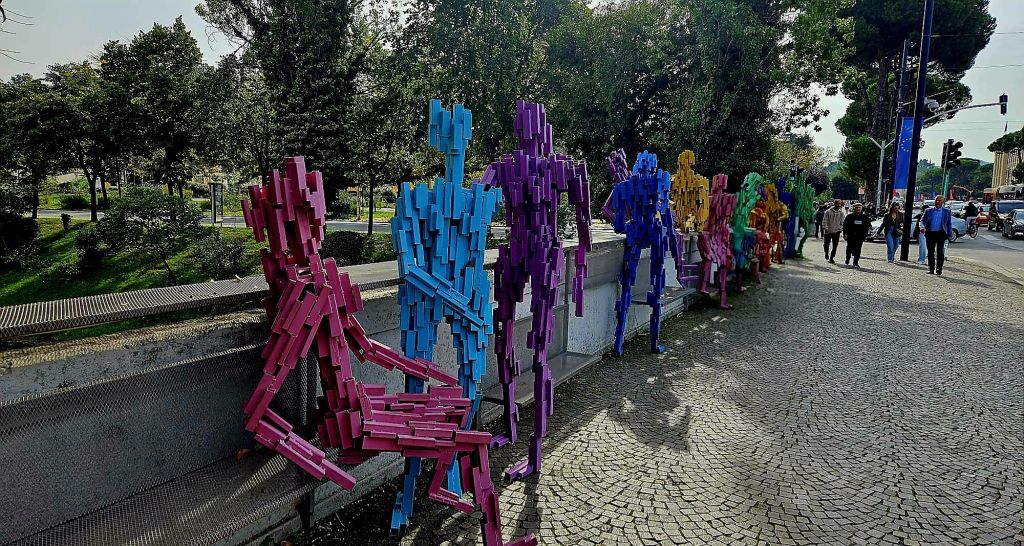
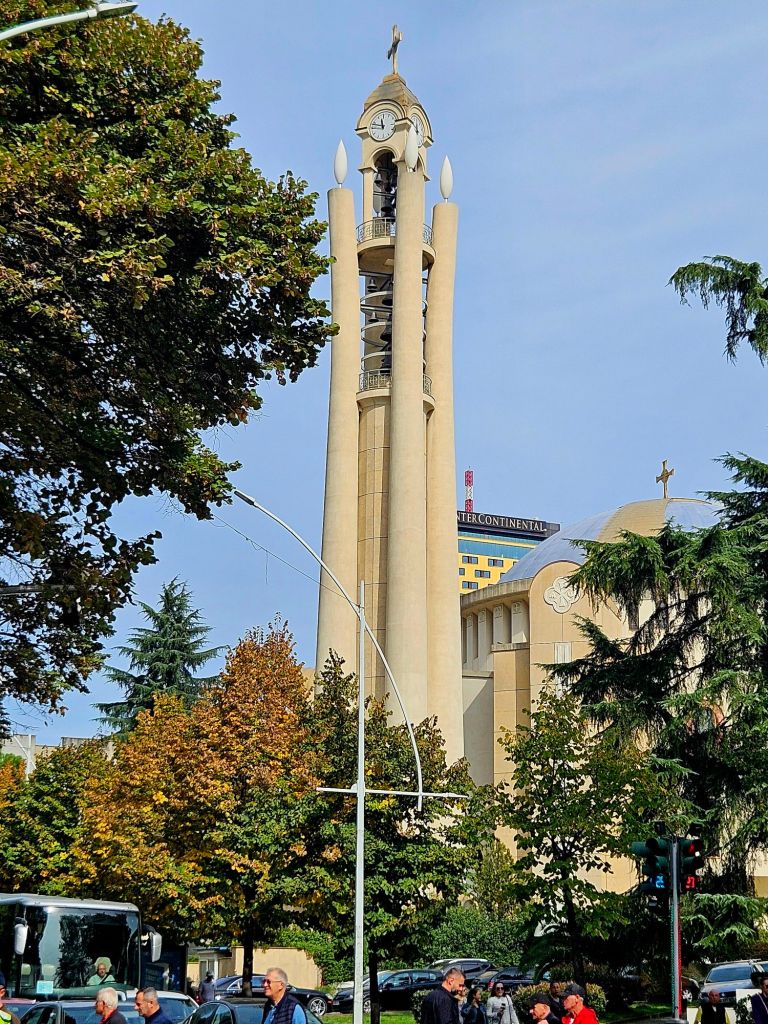
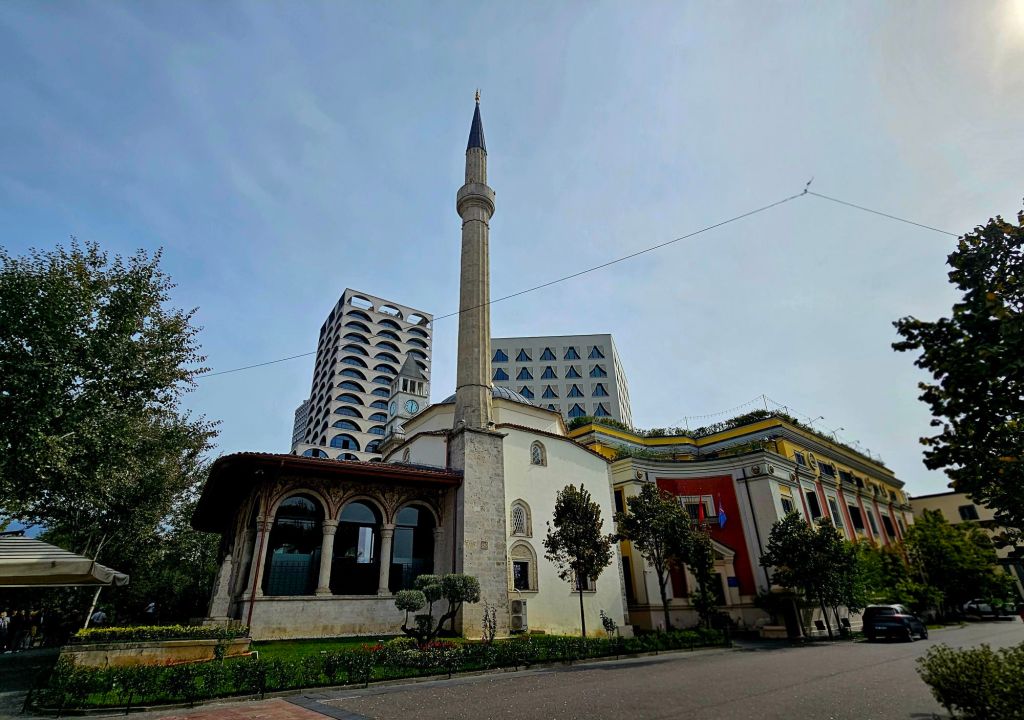
We had a breakfast of crackerbreads, tea and coffee at home again. This time when we walked past the clock tower, it was actually open so we decided to take a look.

The clock tower was built in 1822 by the Ottomans and is 35m high. In 1928 renovations were carried out and the original clock mechanism, which was looted by the Austrians in WWI, was replaced. It was damaged in WWII, but those damages were repaired and it continued to operate from 1946. The bell inside the tower was cast in 1838 and has seven holes in it – most likely a result of damage inflicted in WWII.
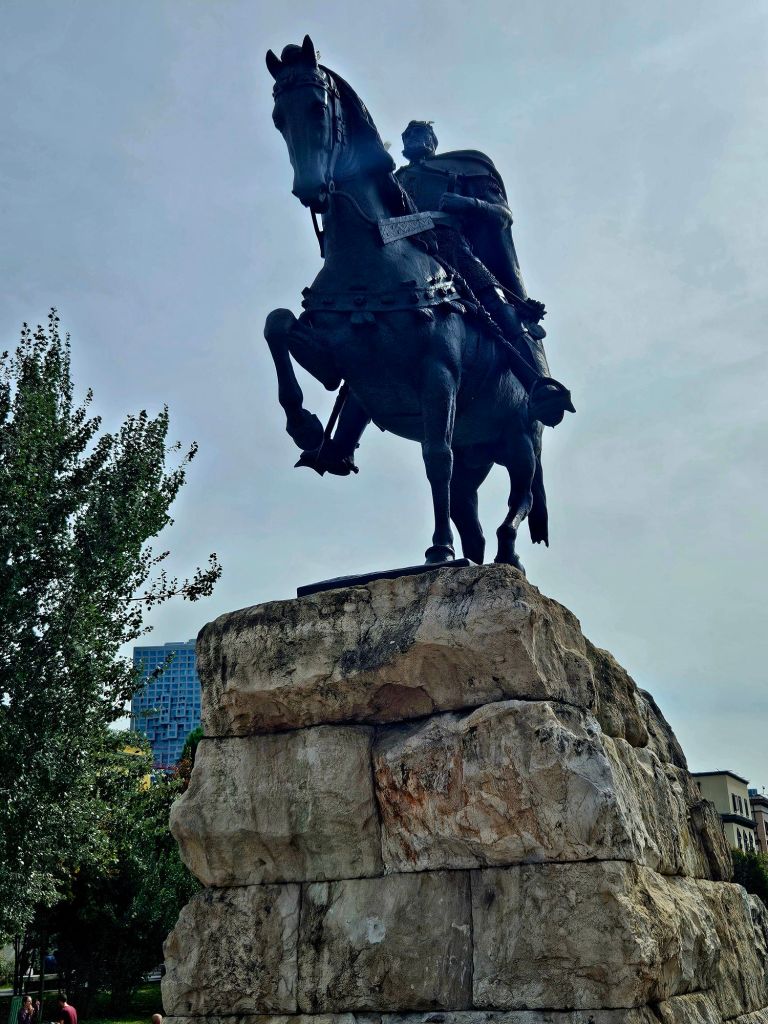
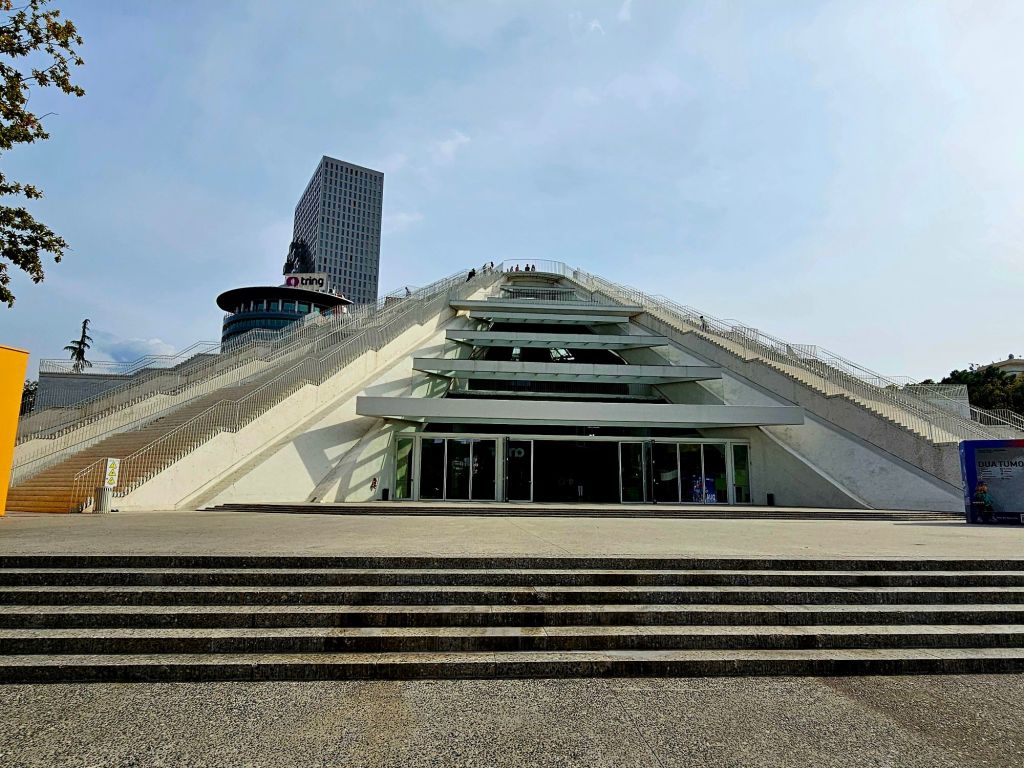
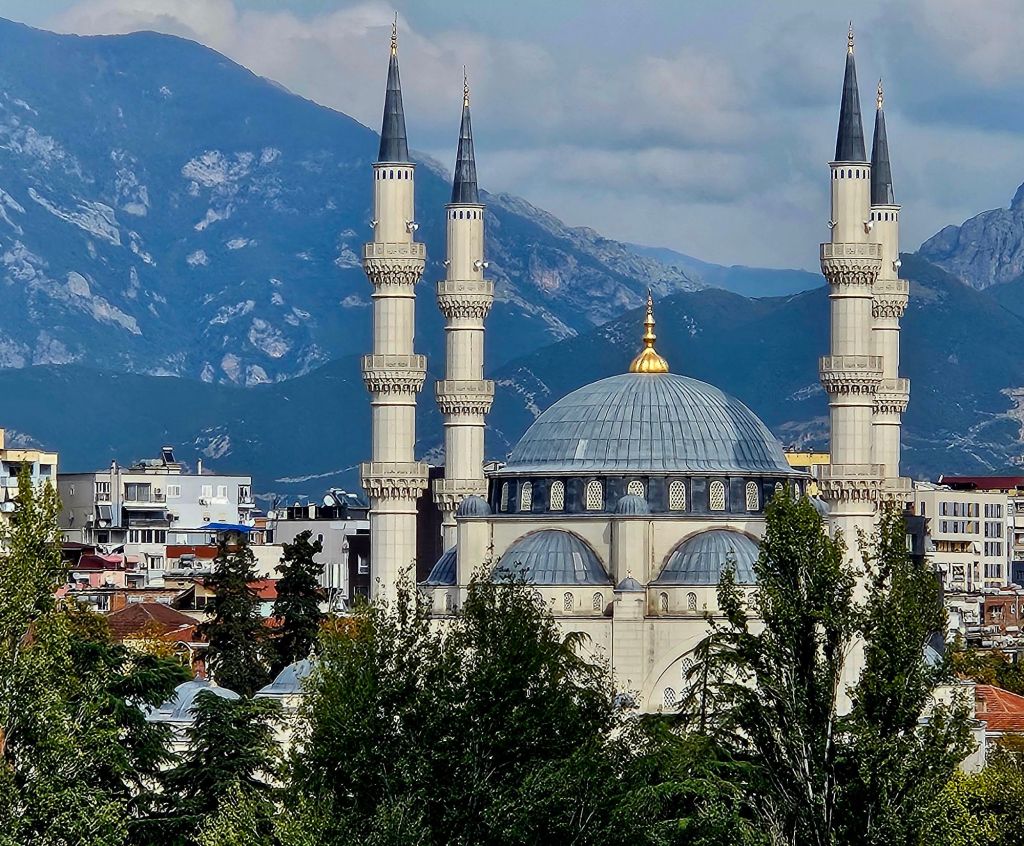
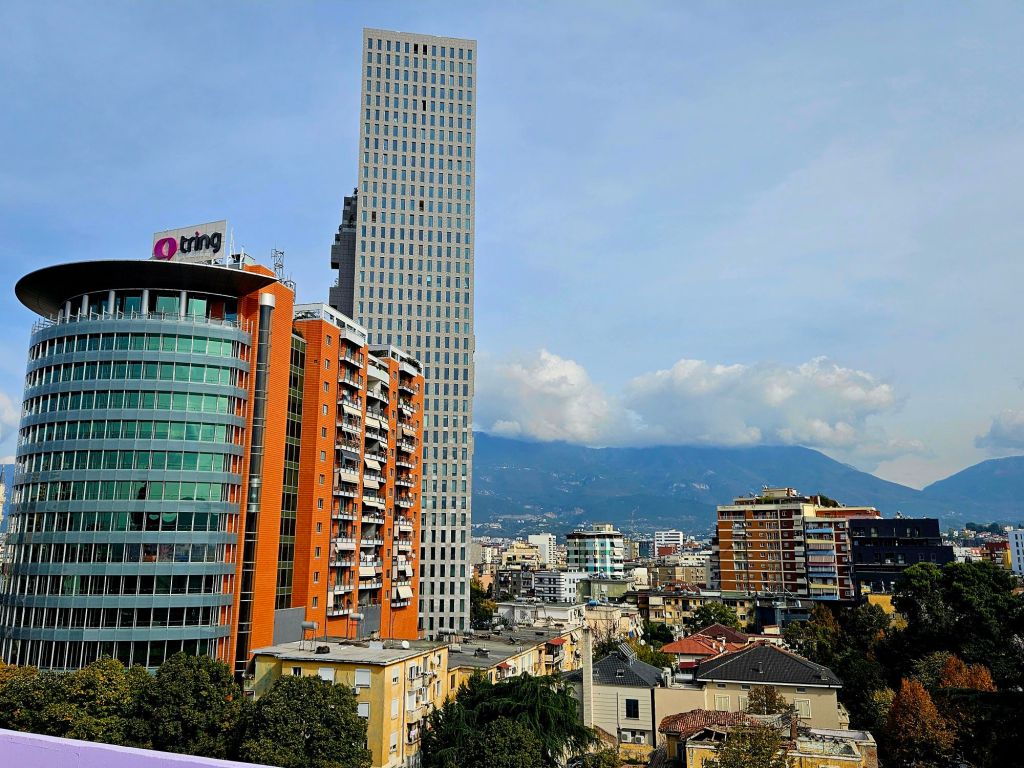
You could get good views from the top, including of Skandenberg square.
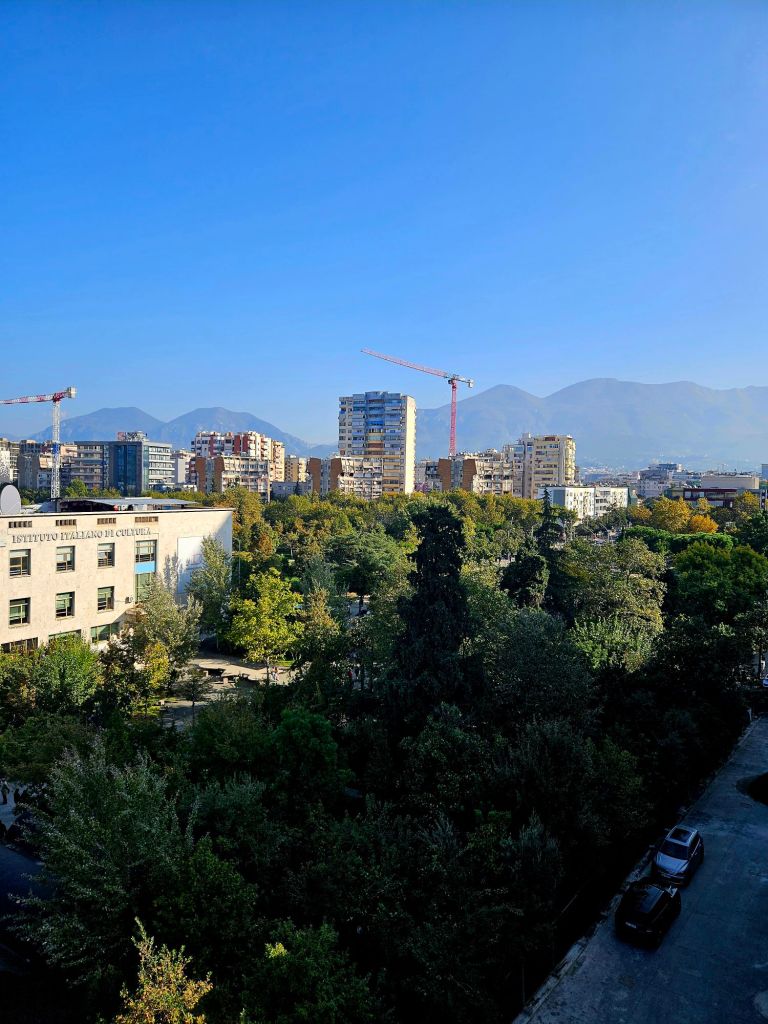
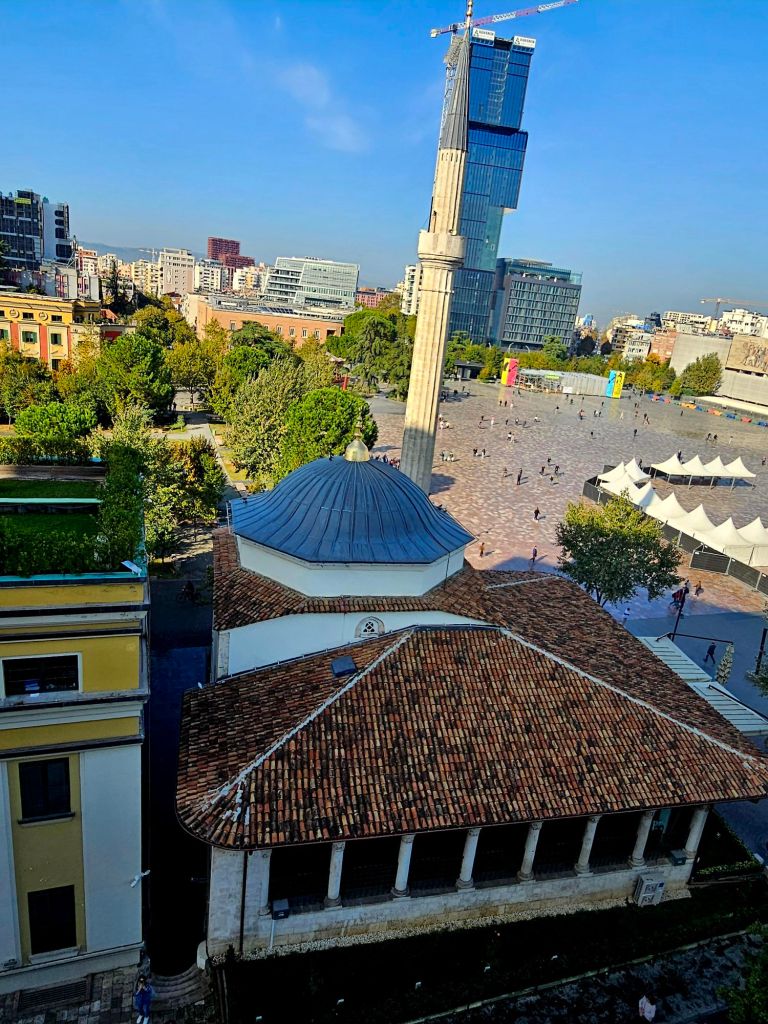
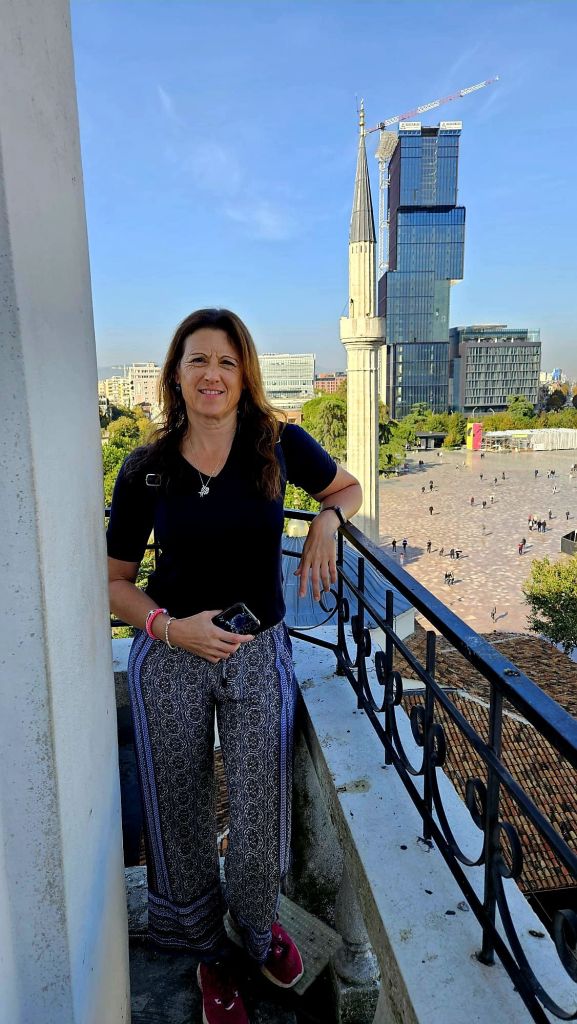





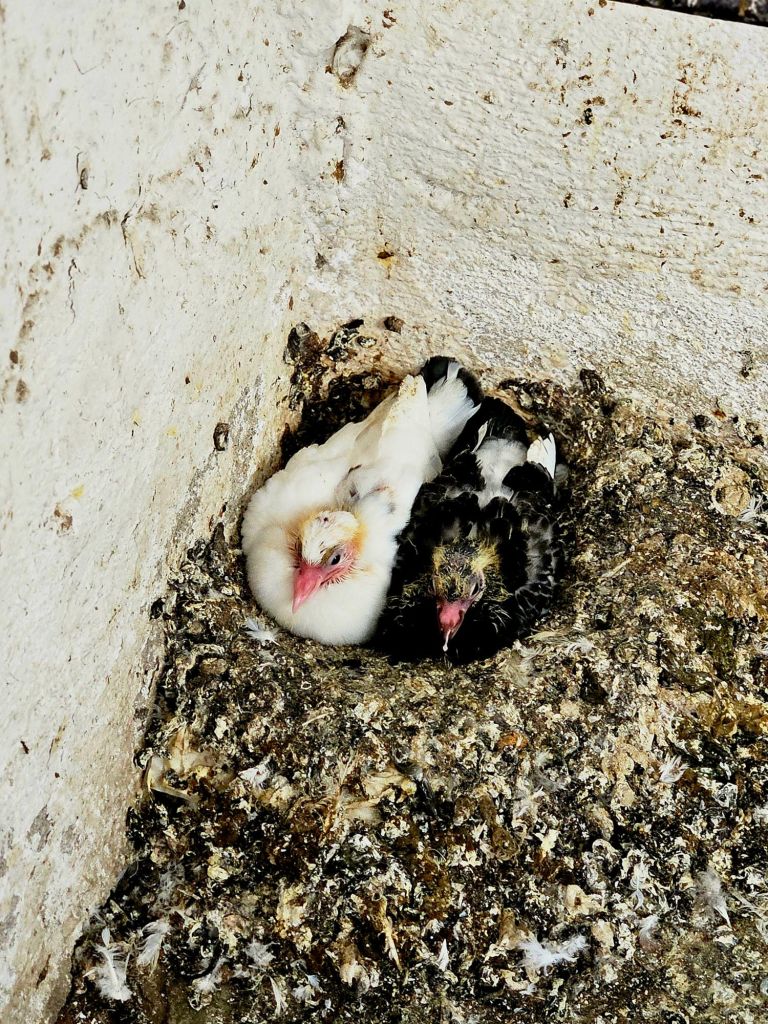
We stayed at the top for a little while, taking photos. On the way back down we noticed pigeons in the corners -basically nesting in their own poop.


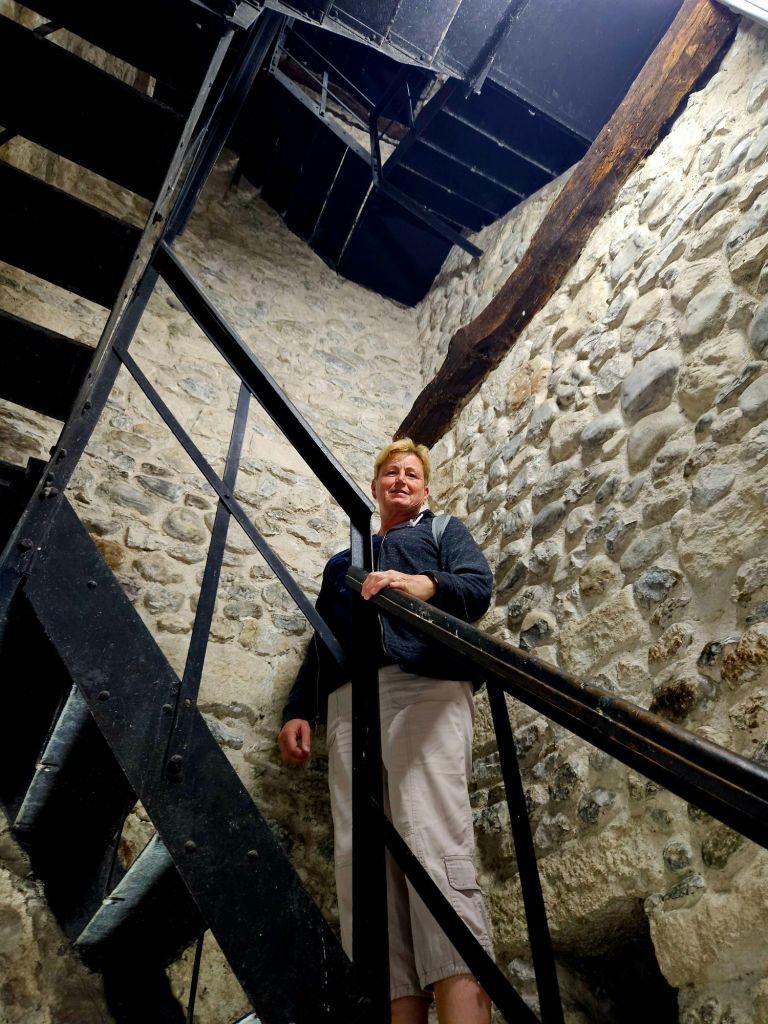
The staircase was very narrow so you had to hope you didn’t encounter anyone going in the opposite direction.
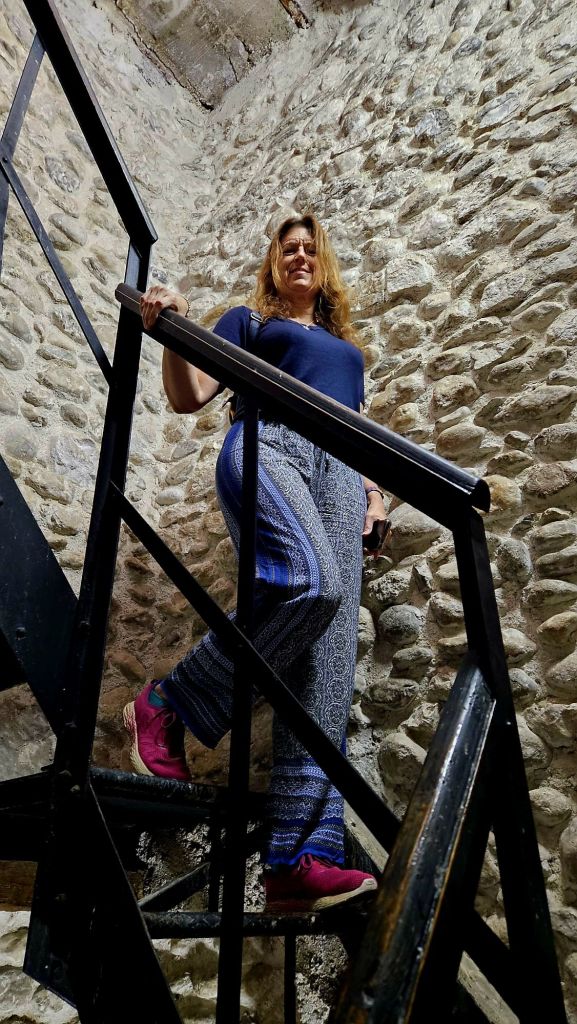


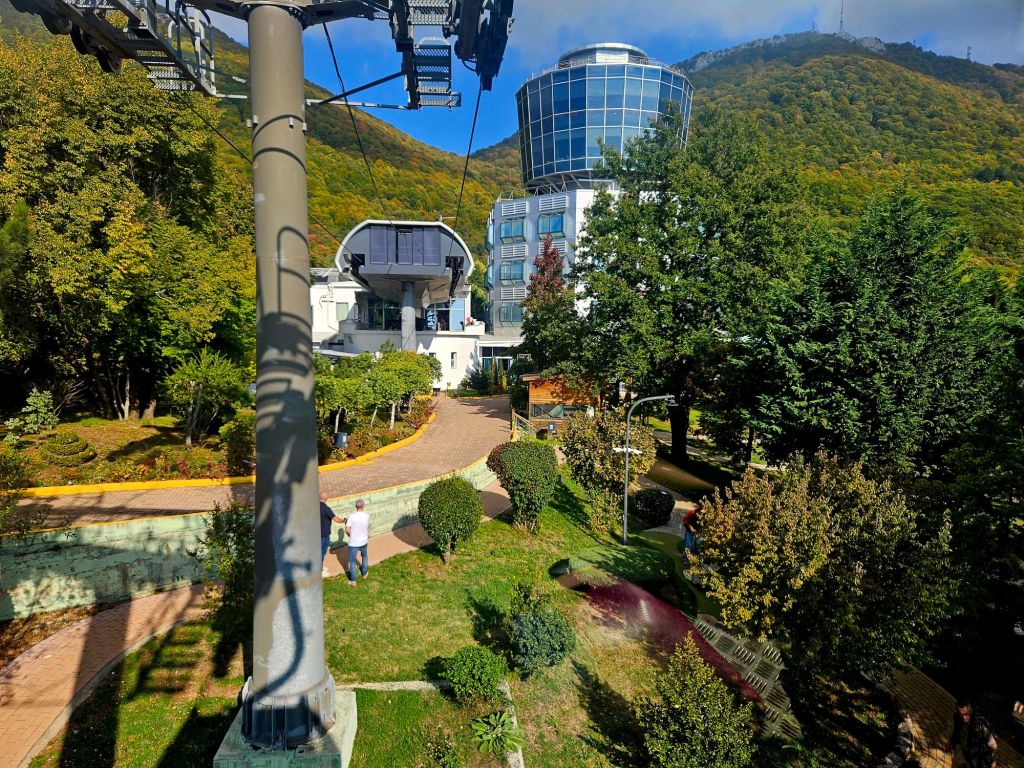
From here we walked down to the bus stop where the bus to Dajti left. The bus fare was extremely cheap, around 40p each for around a 30-45 minute journey. We got off at the stop closest to the Dajti express – the cable car that goes to the top of the mountain.
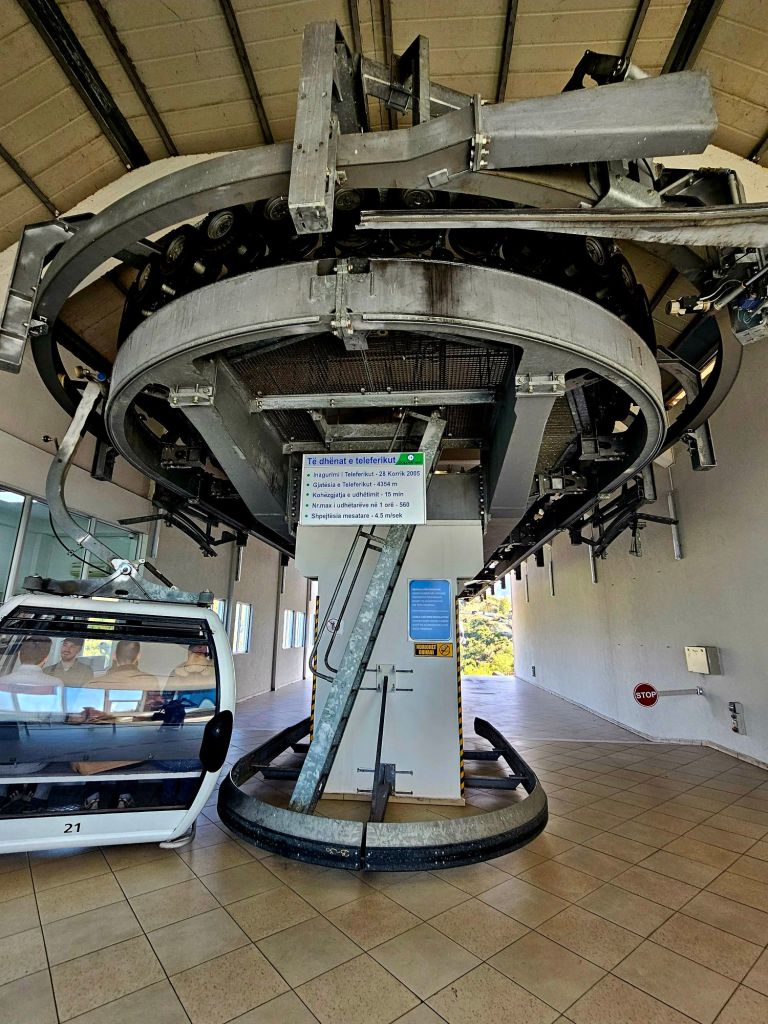

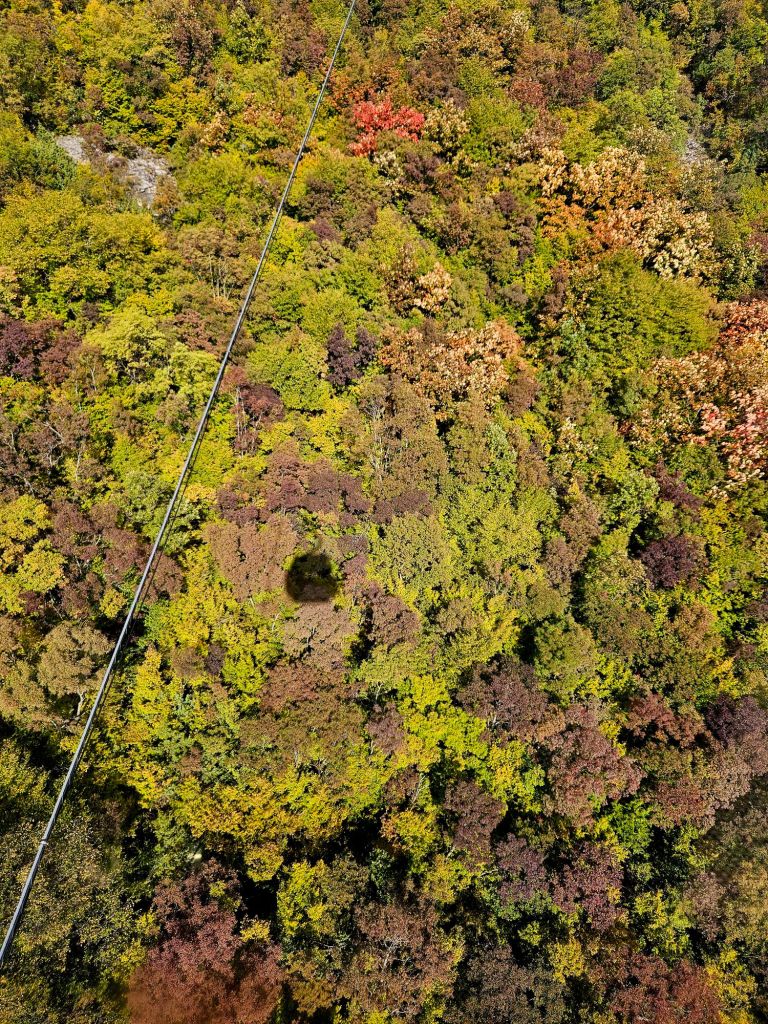
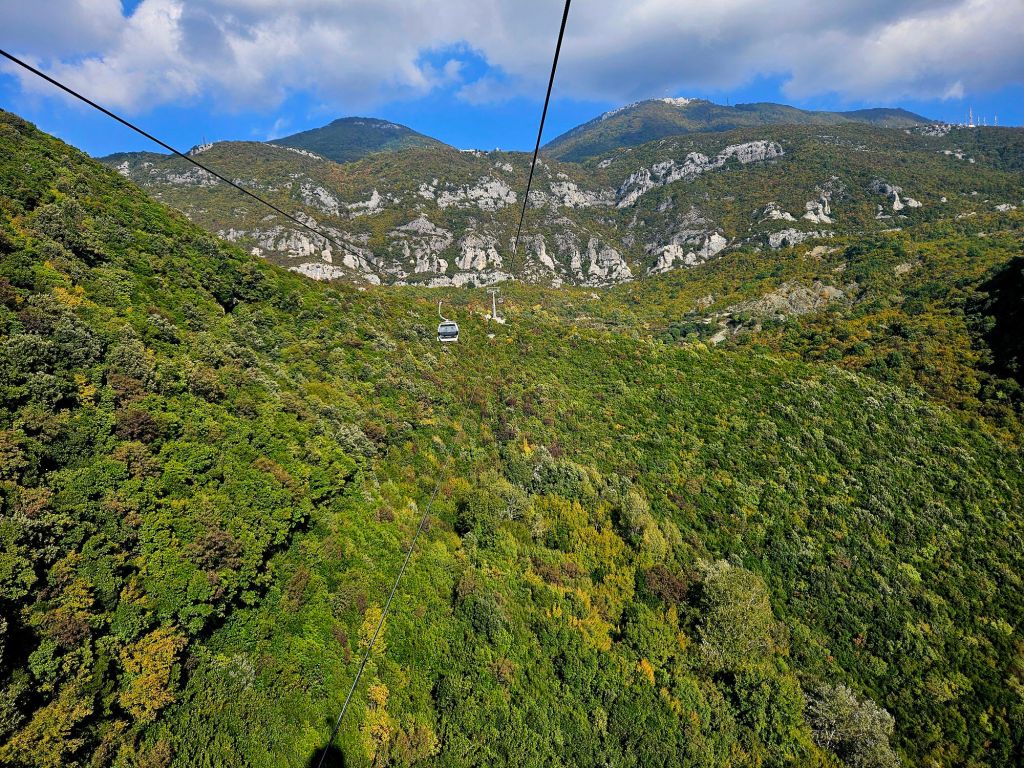
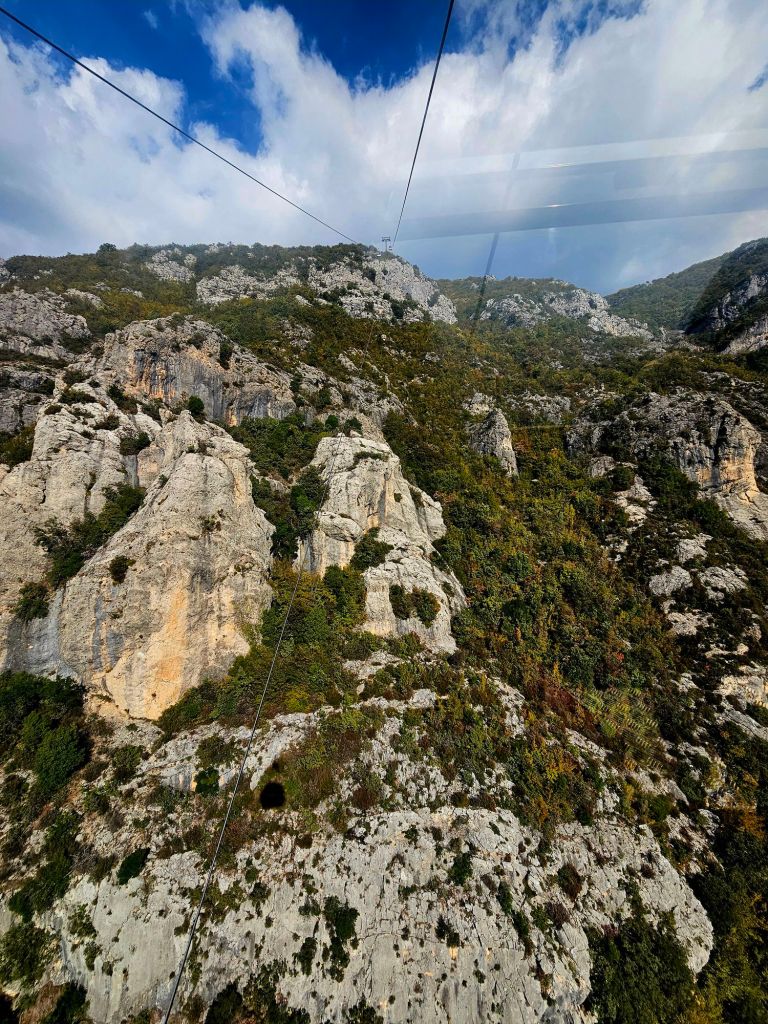
The cable car was built in 2005 and covers a distance of over 4.5km in around 15 minutes. It is the longest cable car in the Balkans. We took loads of photos on the way up.
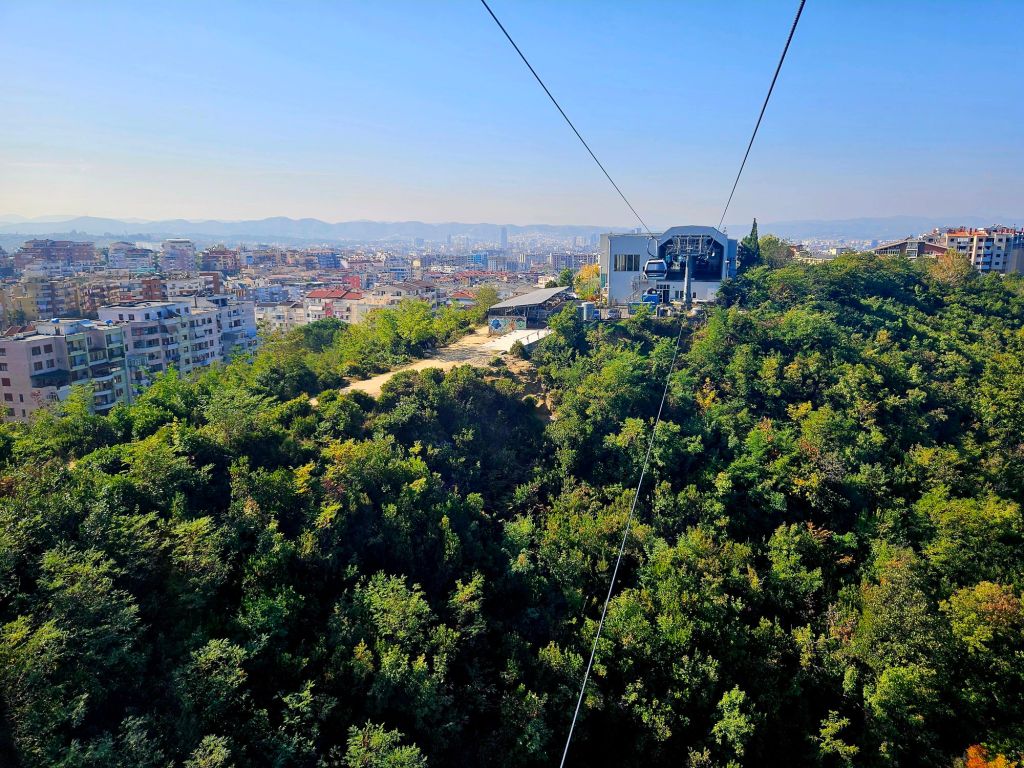
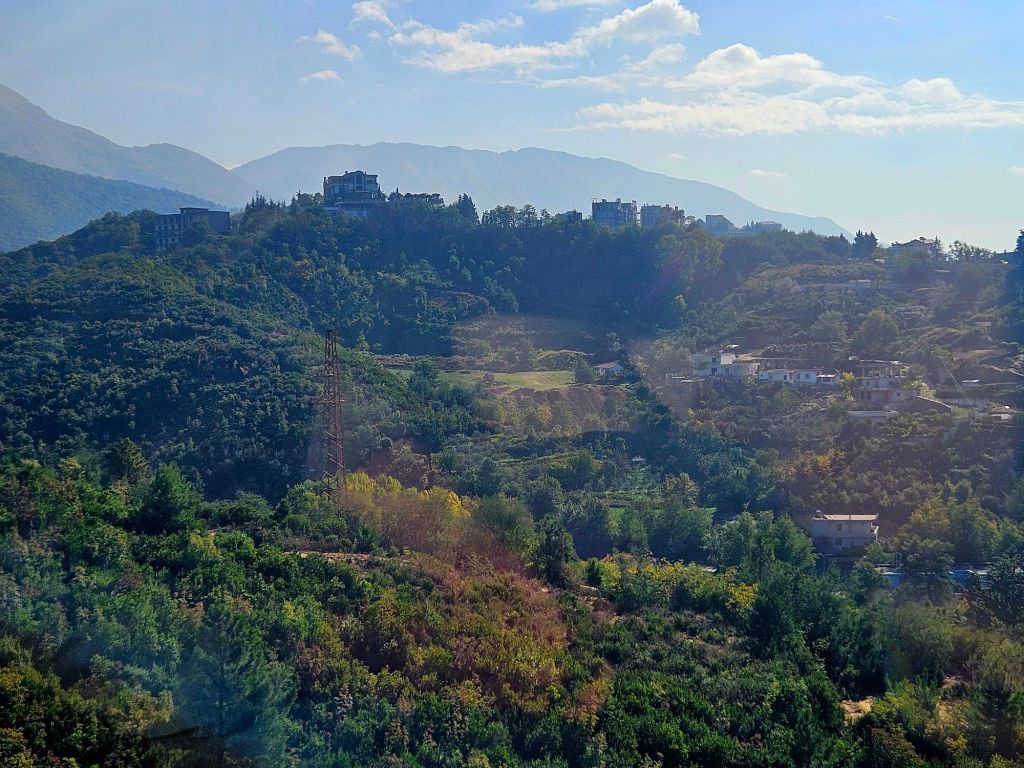
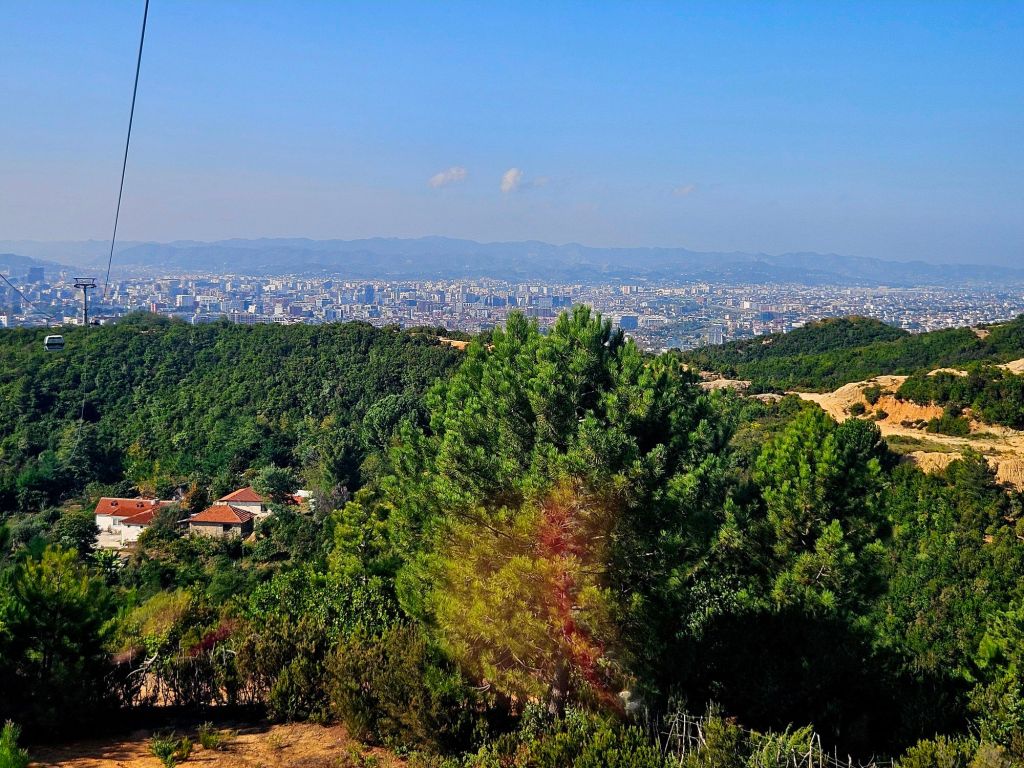
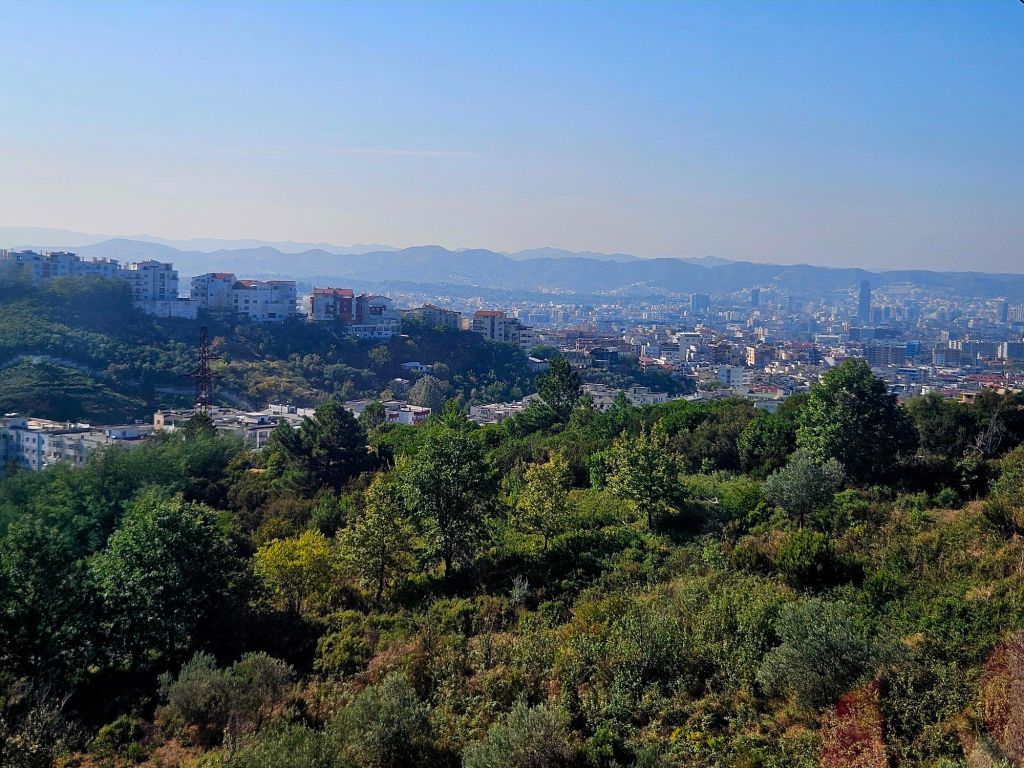
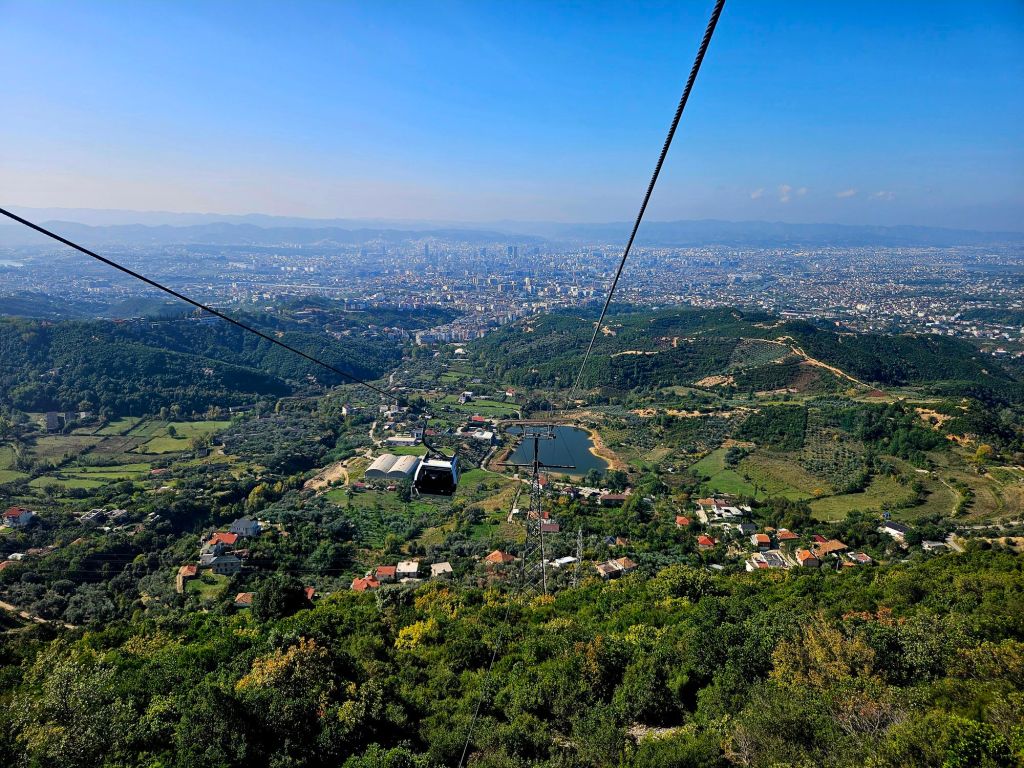
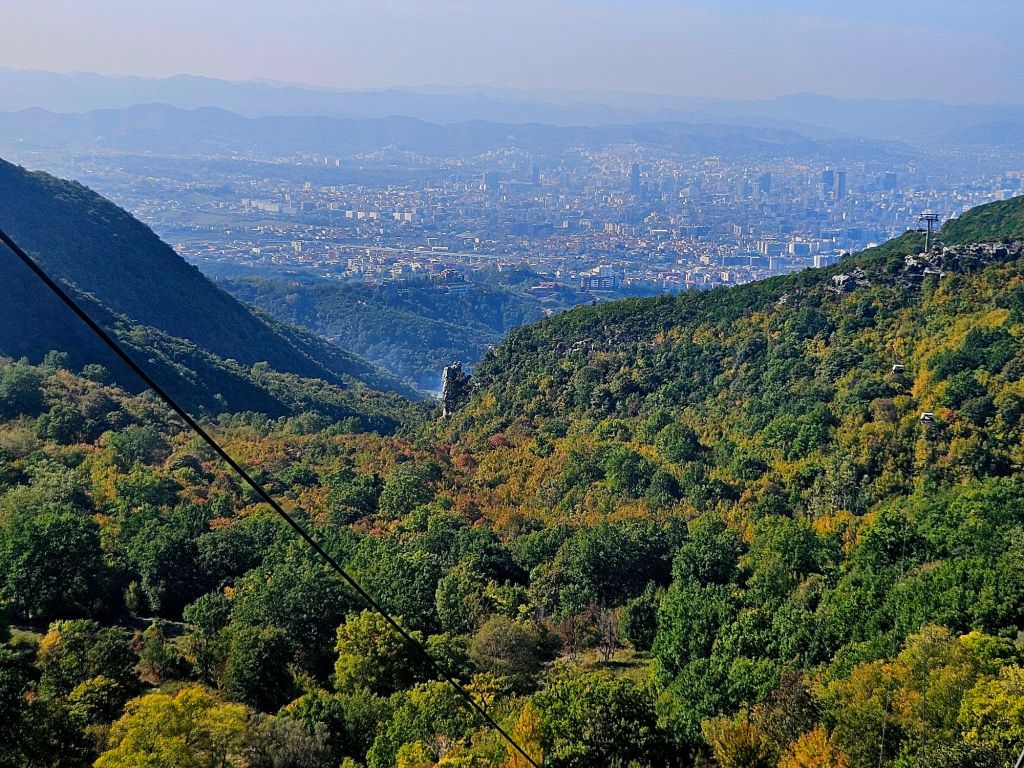
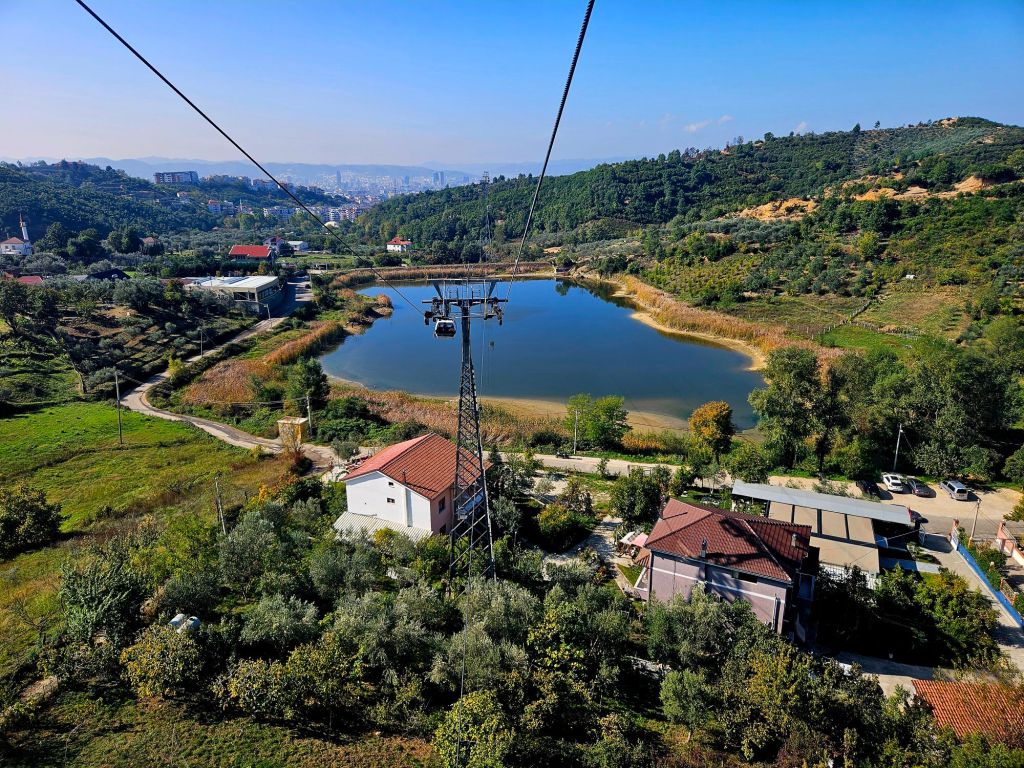
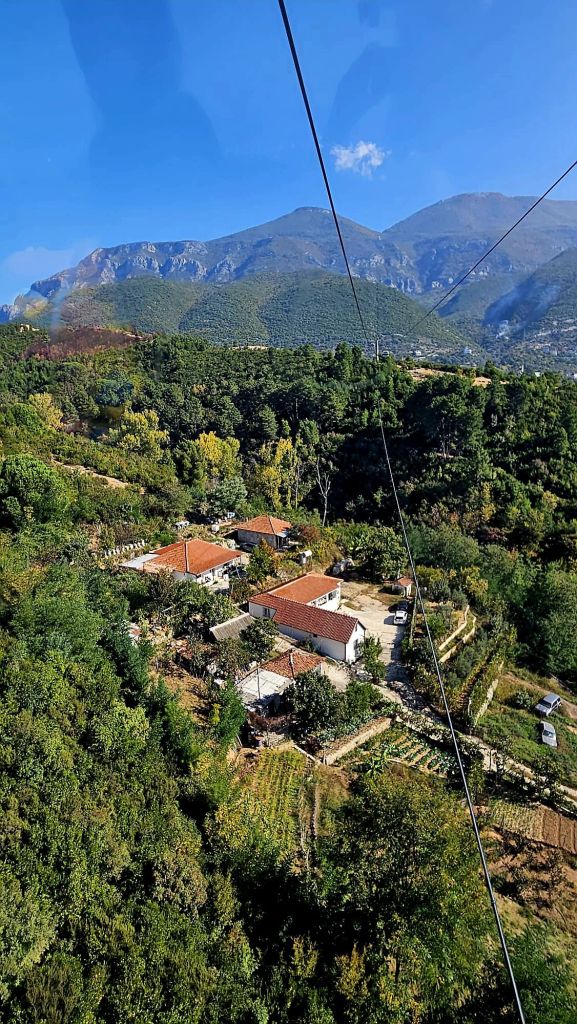








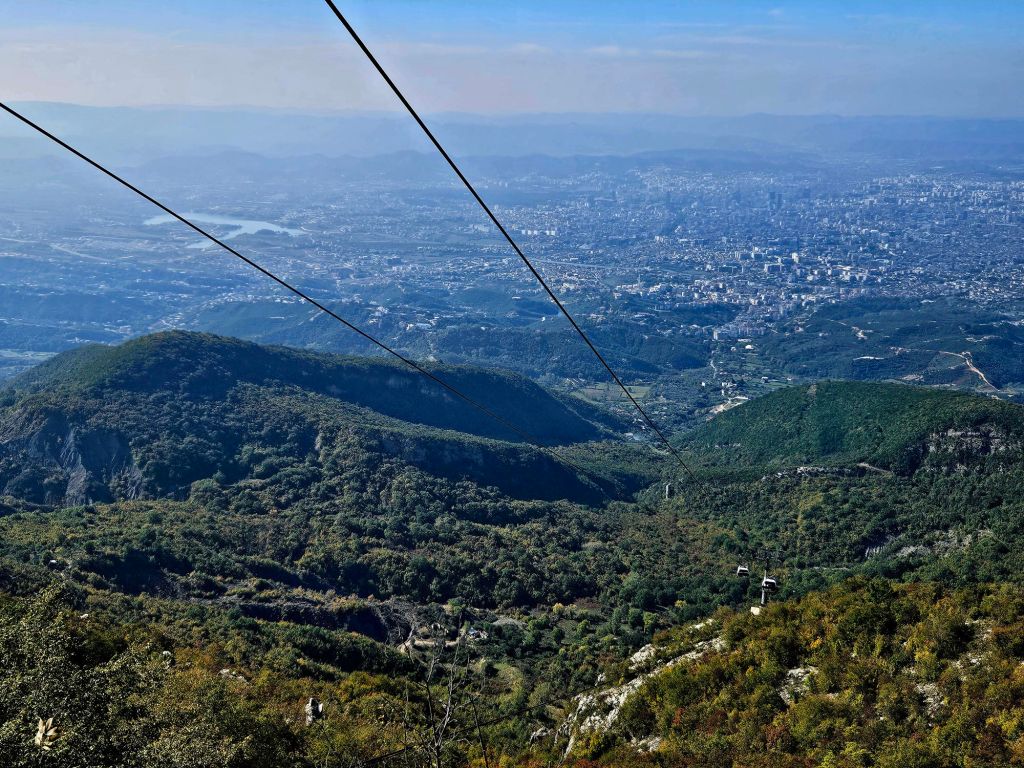
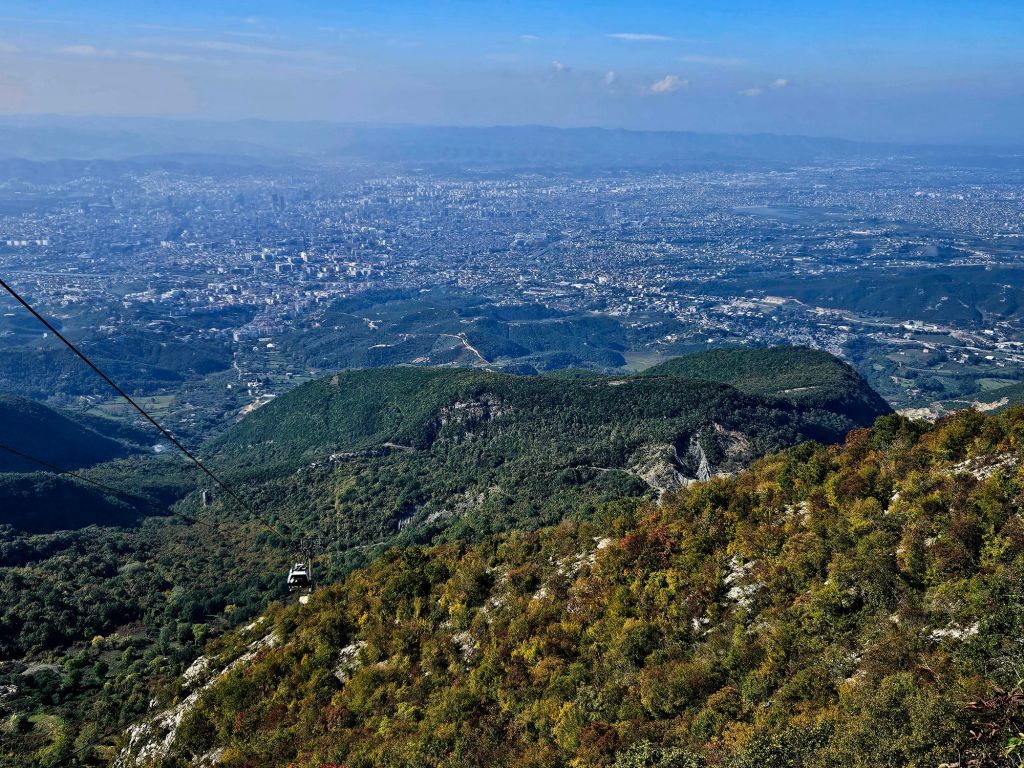
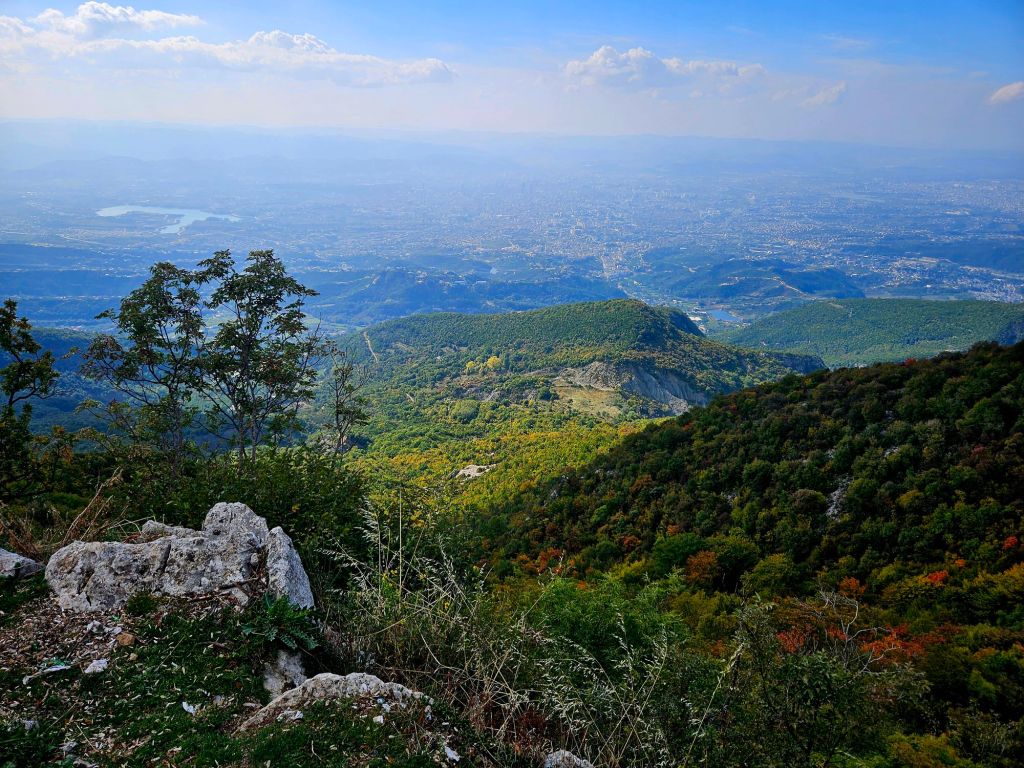
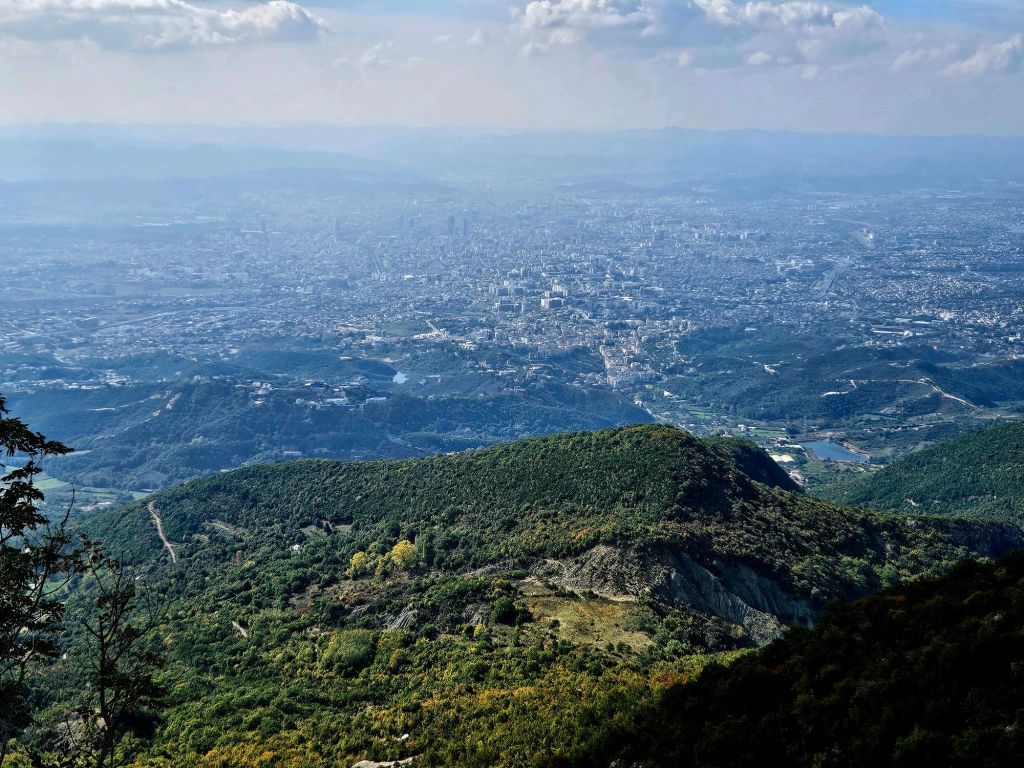
Once at the top, which is 1613m high, we had a little wander around. The mountain is a National Park and was established in 1966. It was originally used as a hunting ground for the aristocracy during the Ottoman Empire. It has since become a symbol of prestige and luxury. Although it was a bit hazy, there were some nice views from the top.


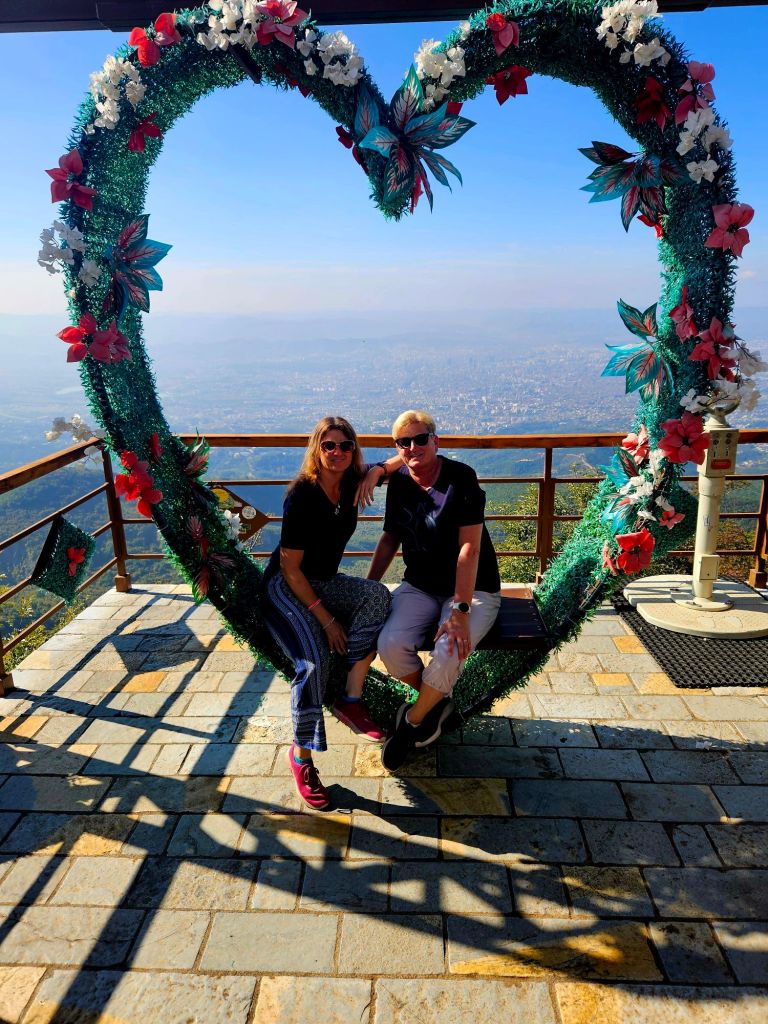
We found the photo corner and posed for some pictures.


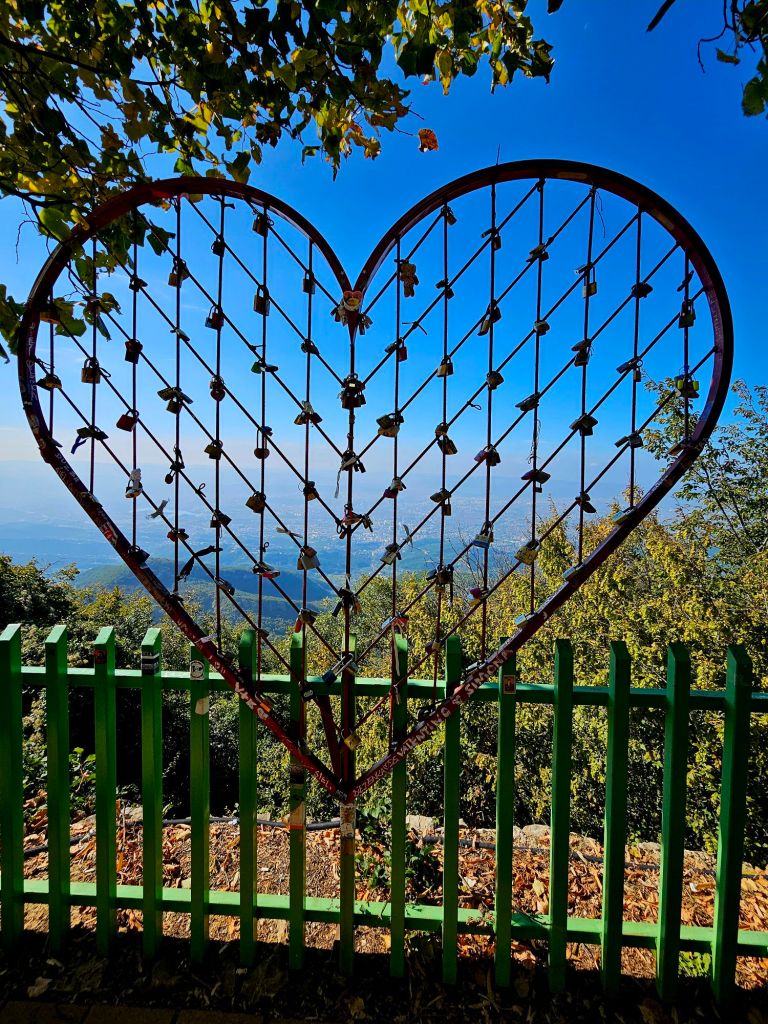
We also found the place to leave your padlocks, but didn’t leave one ourselves.

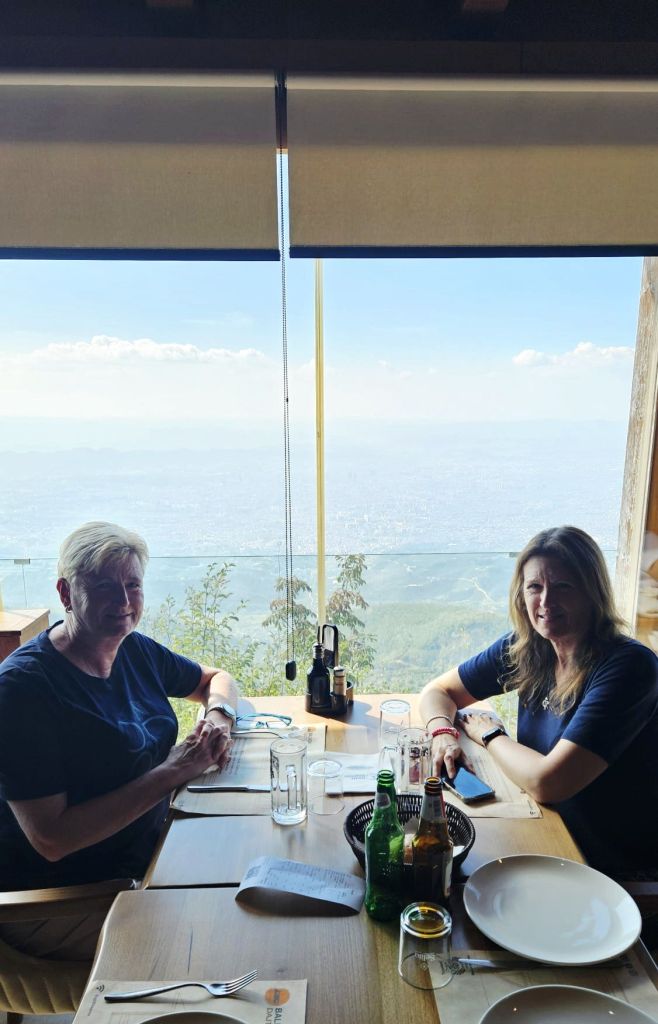
And then it was time for lunch. We had intended to go to the Dajti tower for a drink, some snacks, and the views, but unfortunately it was shut.

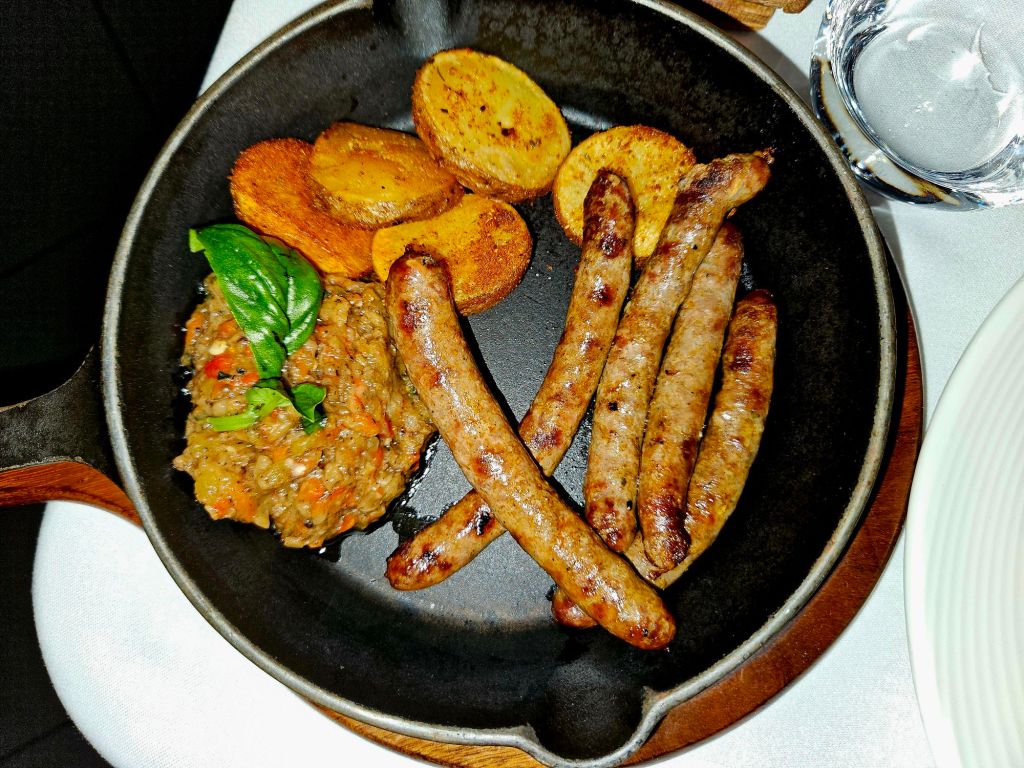
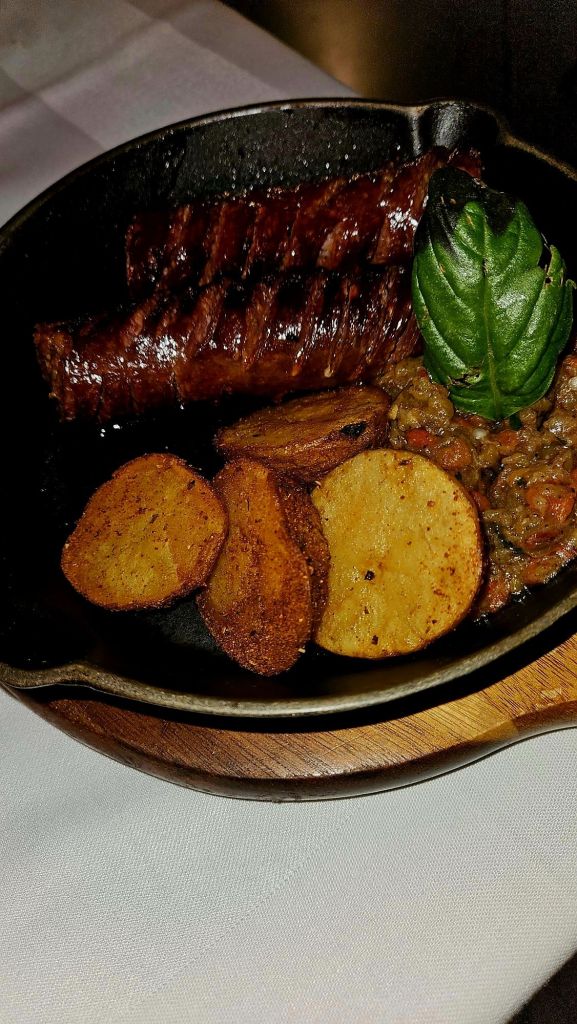
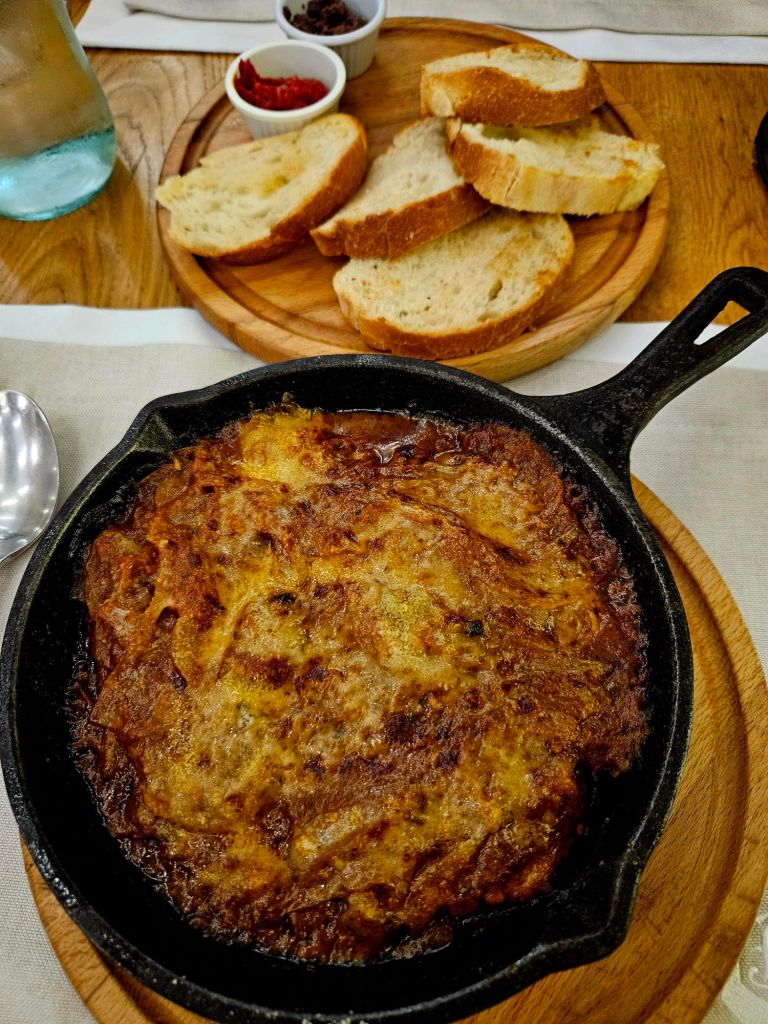
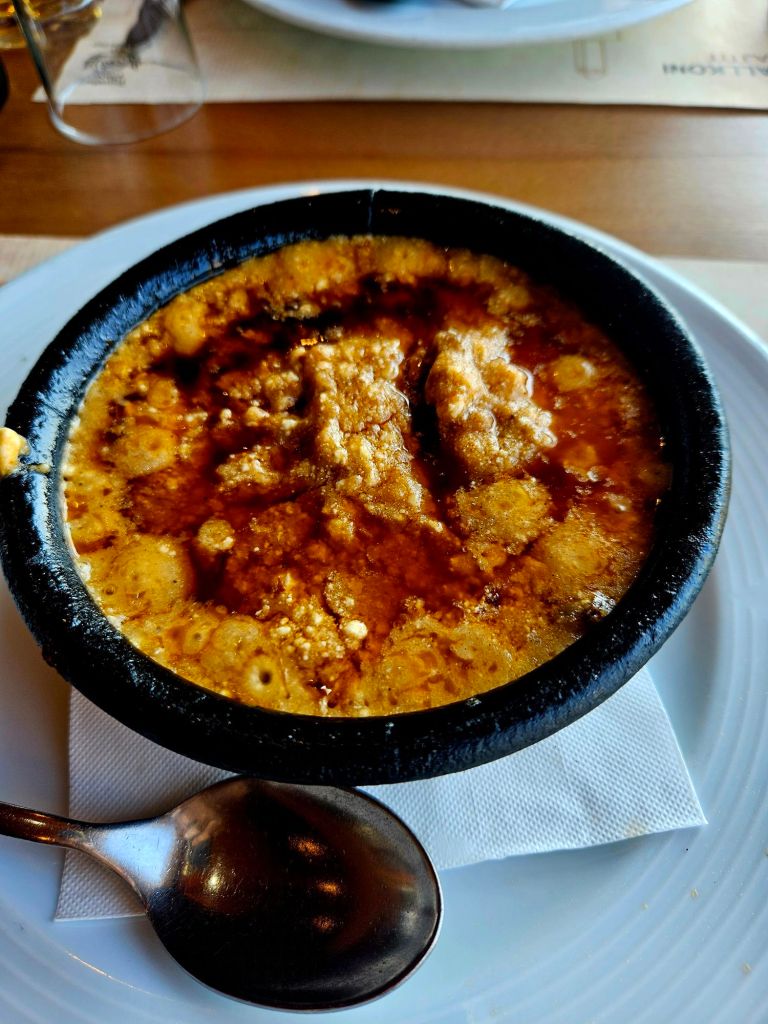
So we went to the Ballkoni Dajti Restaurant instead. We both ordered the beef tava and an Albanian beer. Tava is an Albanian casserole made with meat, yoghurt and eggs. It was quite fatty, very hot, and extremely delicious.
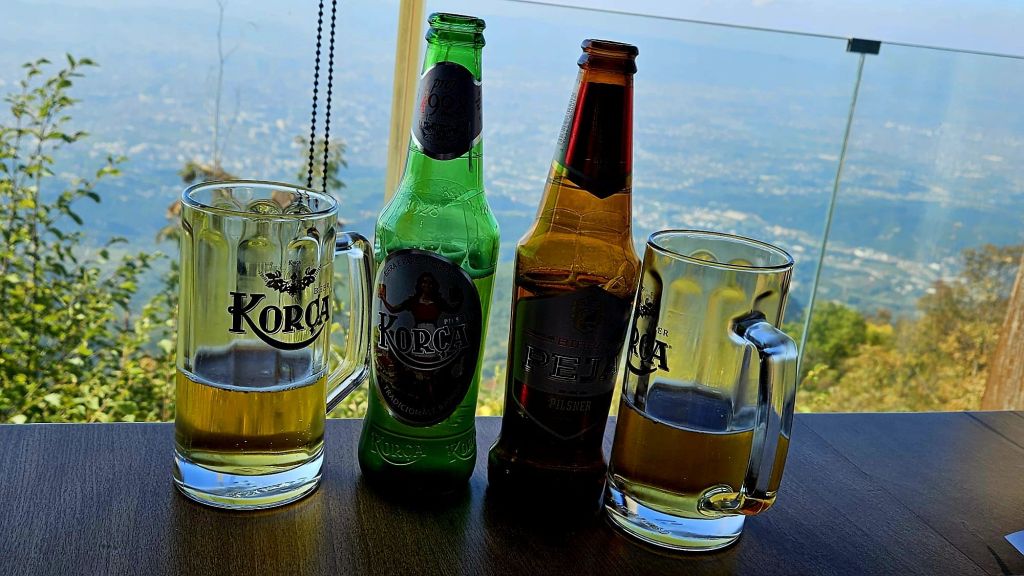



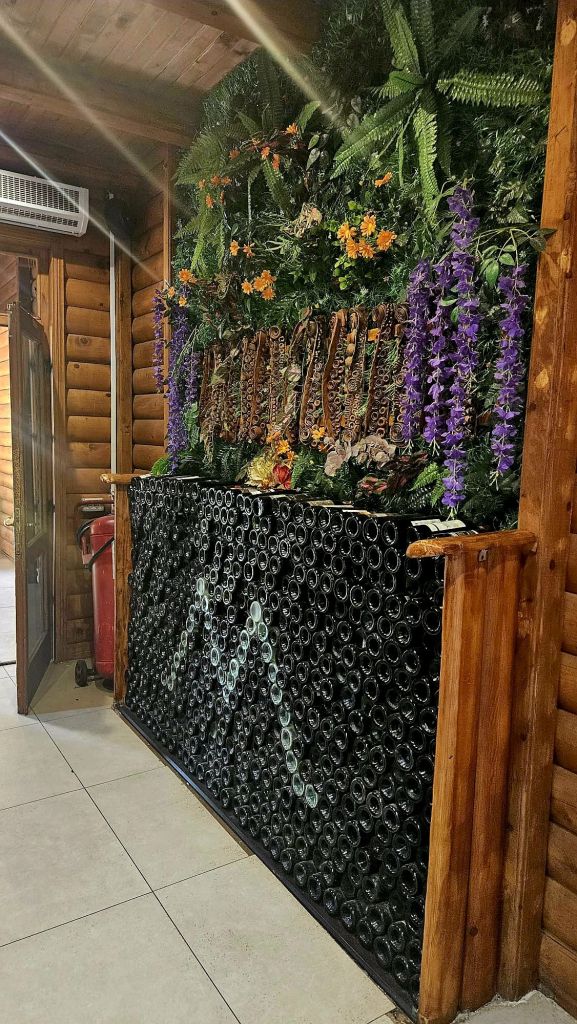
The restaurant is built in the style of a log cabin and looks very Scandinavian.

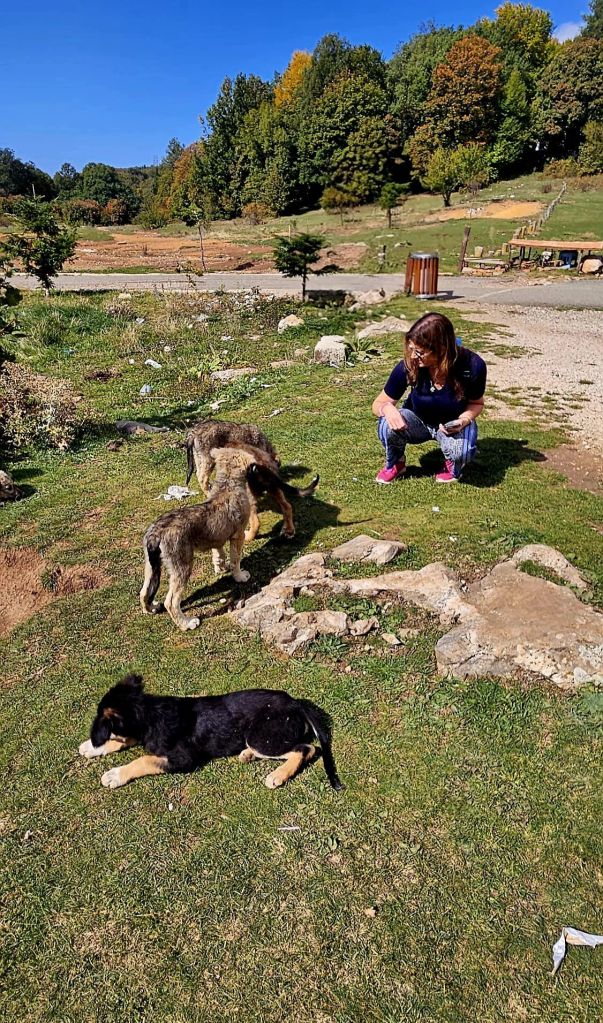
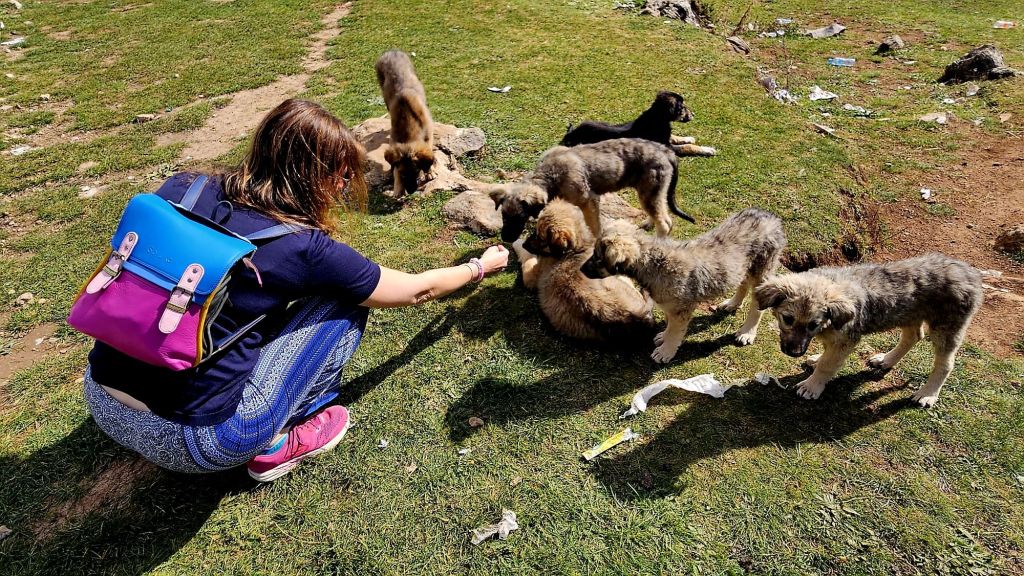
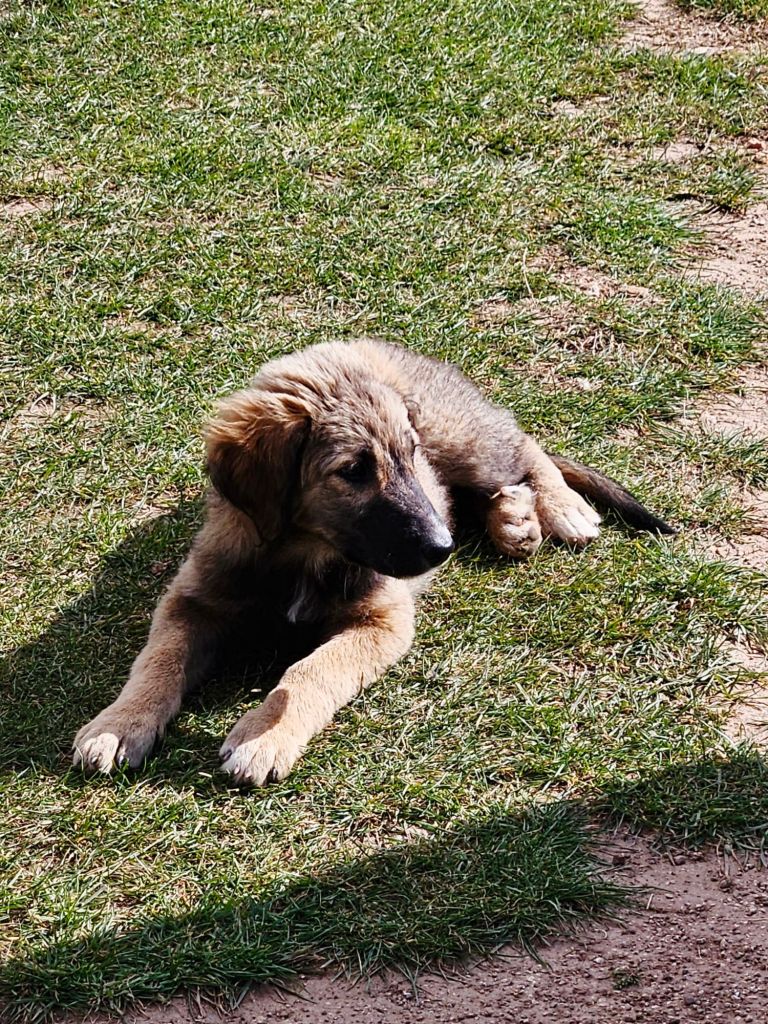
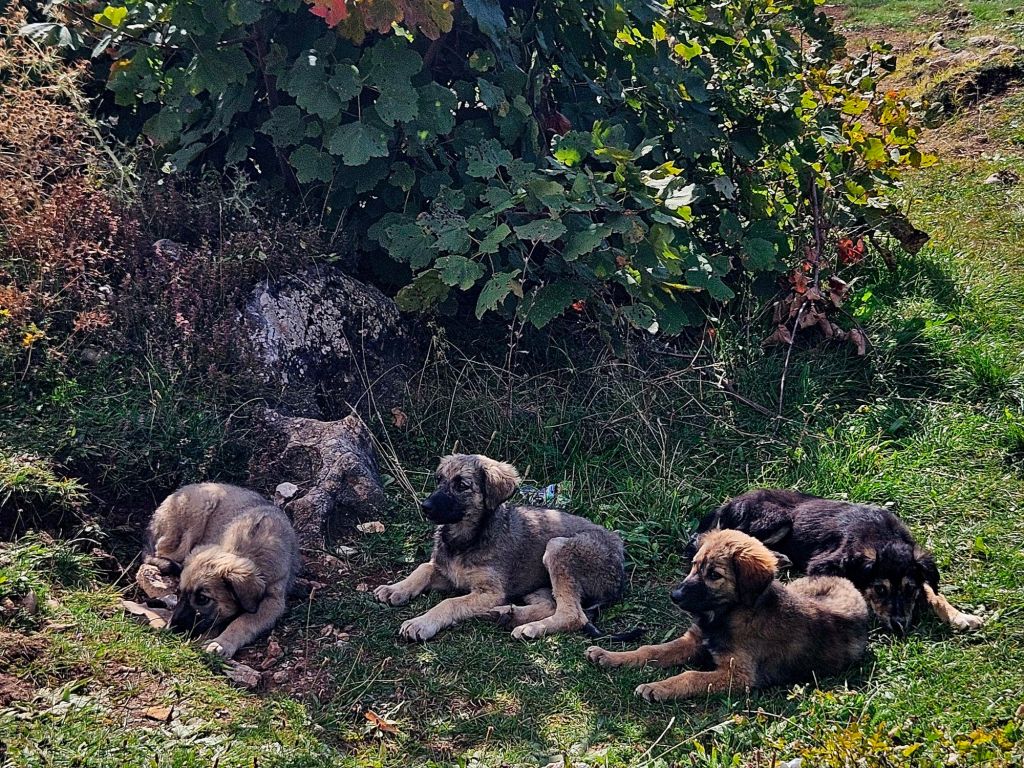
From here we decided to go for a walk through the National park. There are lots of different routes to choose from but they all start at the car park. And just by the car park we saw some gorgeous puppies, who were very friendly. Unfortunately we didn’t have any snacks or food for them, but they came over for a pet or two.




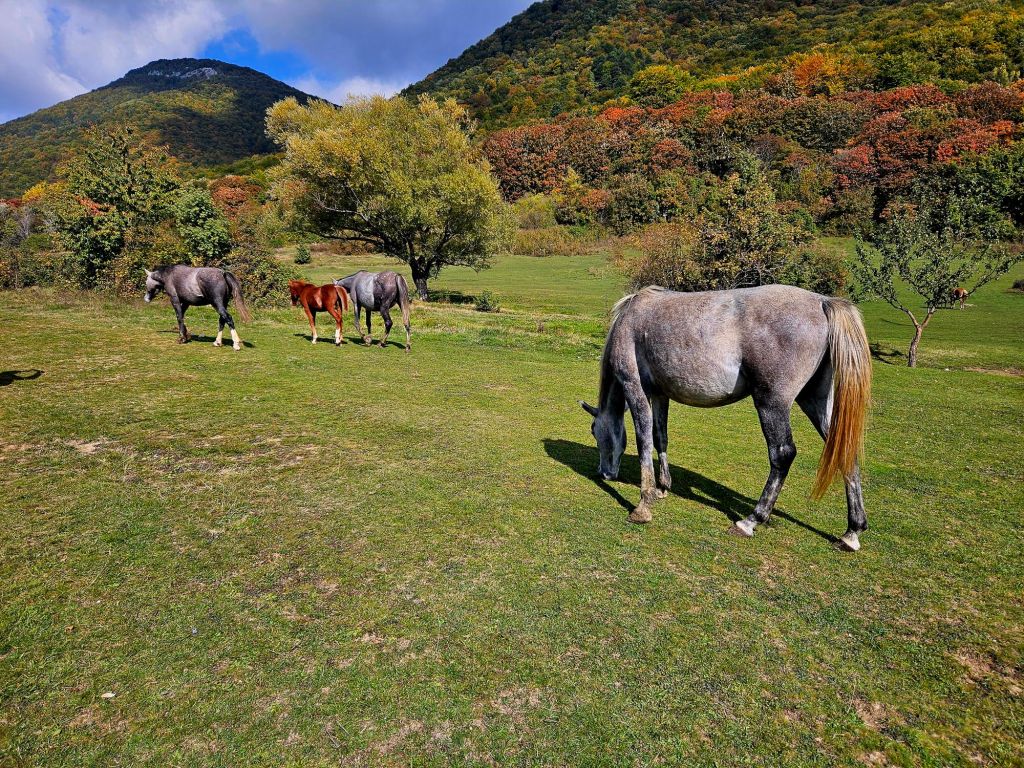
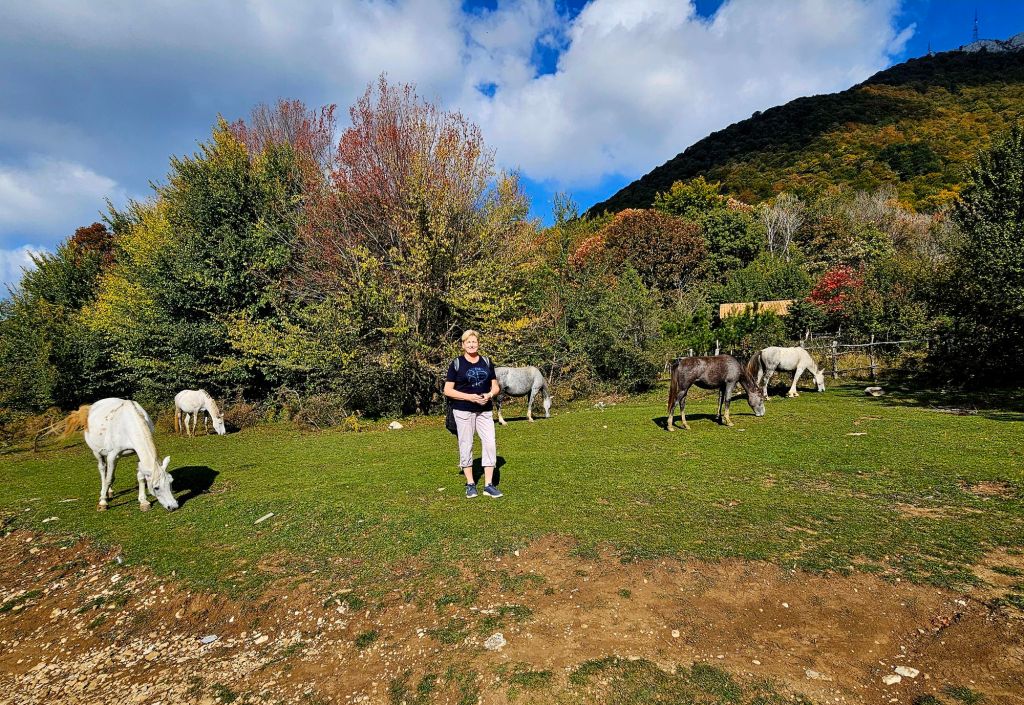
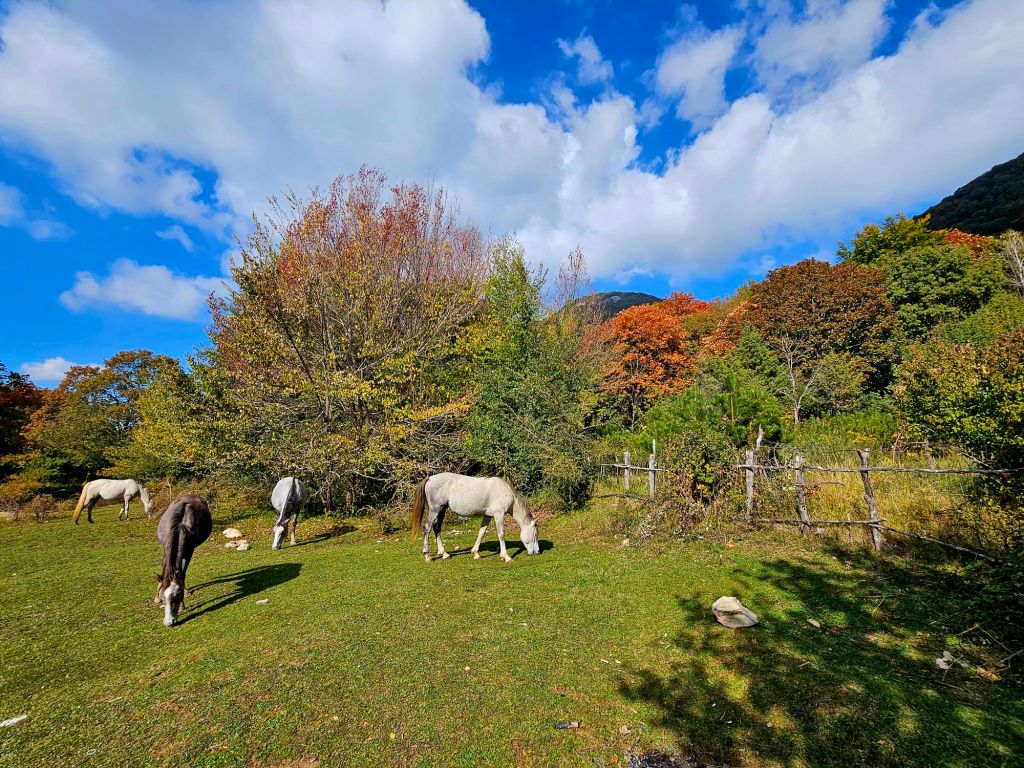
We had to abandon the first route we tried to take as it went through a military zone that members of the public were not allowed to enter. The route we did take took us through some open fields with horses and with some lovely views.




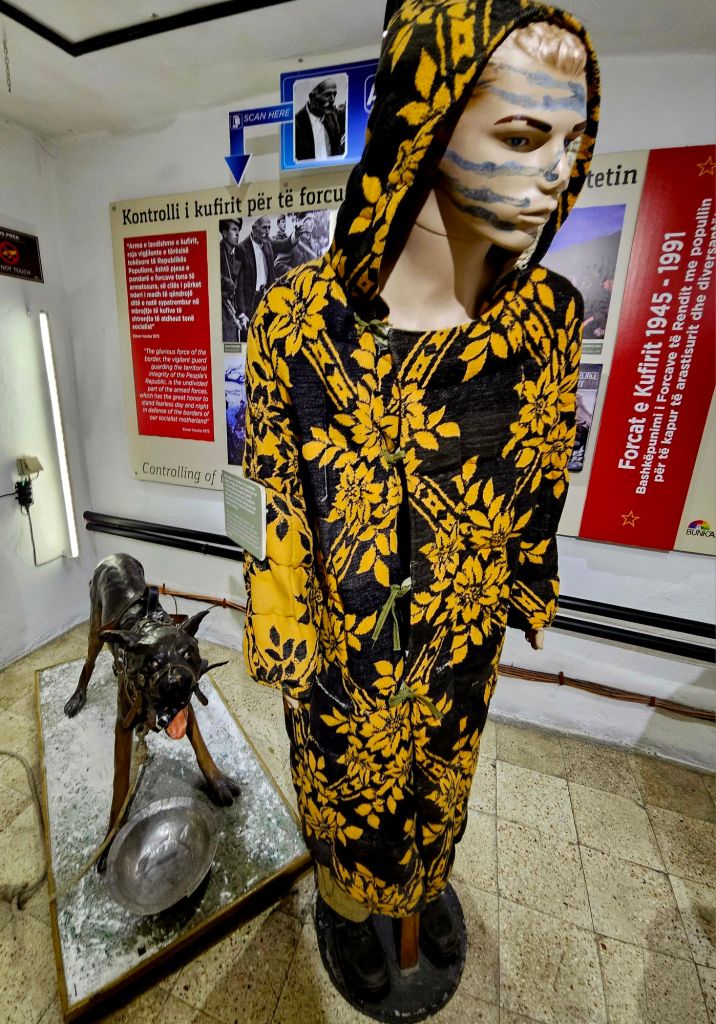
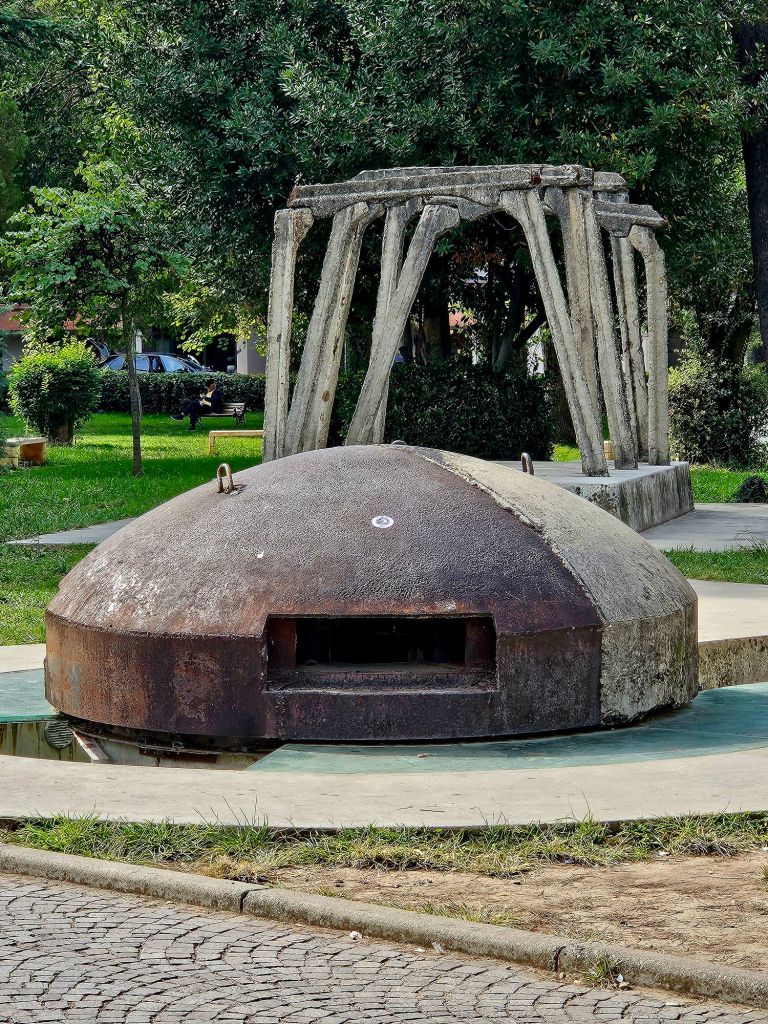
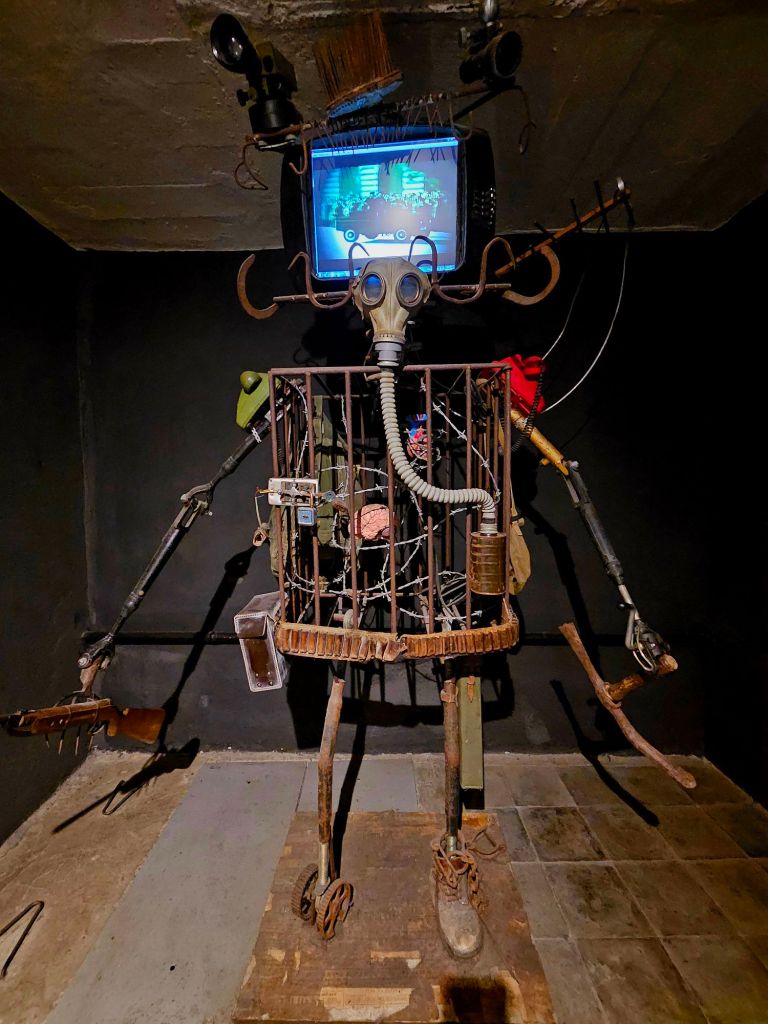
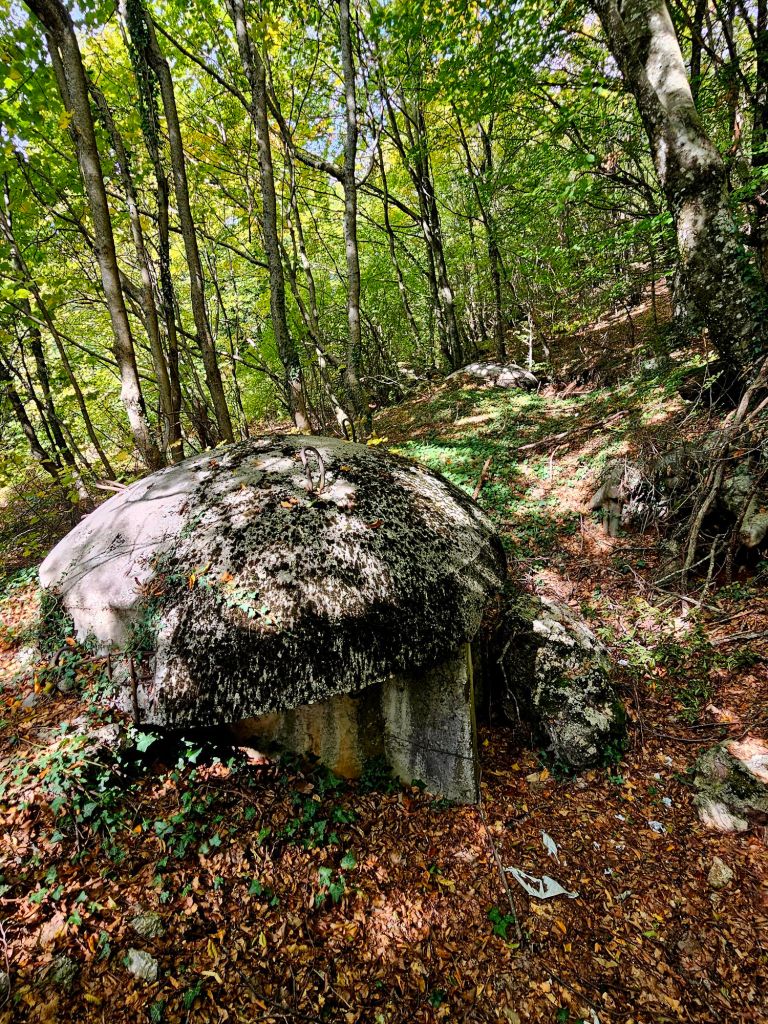
Throughout the national park we came across quite a lot of bunkers. Enver Hoxha was convinced that all of the neighbouring countries wanted to invade Albania so he set up a bunker- building programme. It’s estimated that around 170,000 bunkers were built, most of them being the QZ (firing position) model, designed to hold one or two people. Hoxha called on the mobilisation of the general population, most of whom had to do basic military training each year, to form a resistance in their tens of thousands if needed. From the age of twelve children were trained to go to the next bunker in case of emergency and to defend it. All families had to keep the bunkers clean and ready for action in the vicinity of their homes and apartments. At least twice a month, combat exercises took place, each lasting up to three days. Ironically, during Hoxha’s reign there was not a single armed conflict.
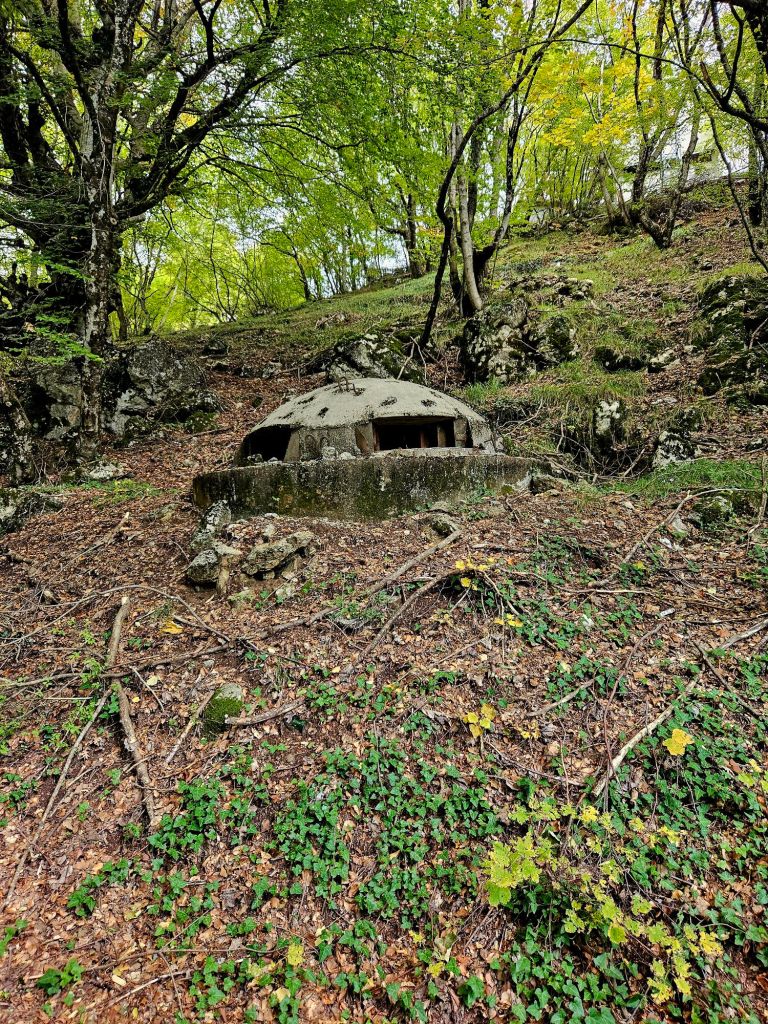
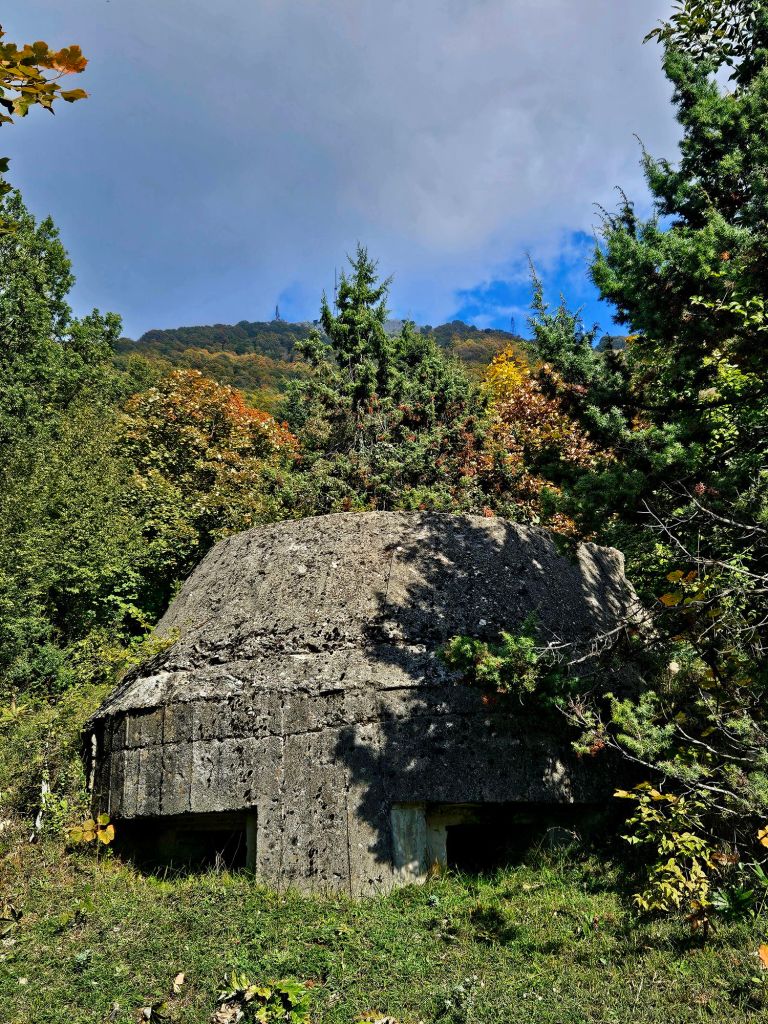
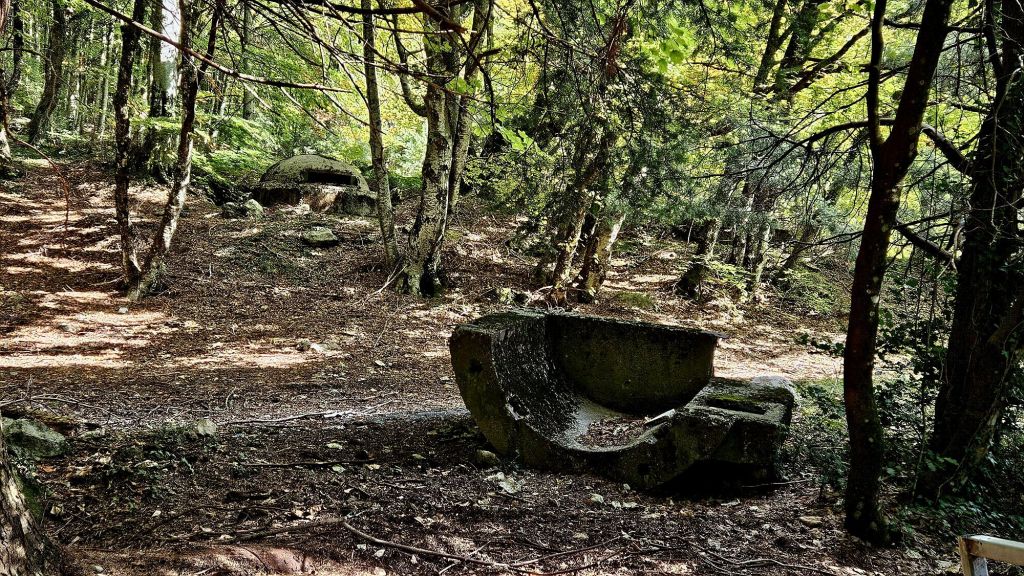






The cost of building the bunkers was significant and took funds away from resident housing and broken roads. It’s believed that 70-100 people died each year whilst building the bunkers due to forced labour, dangerous conditions and poor working practice.
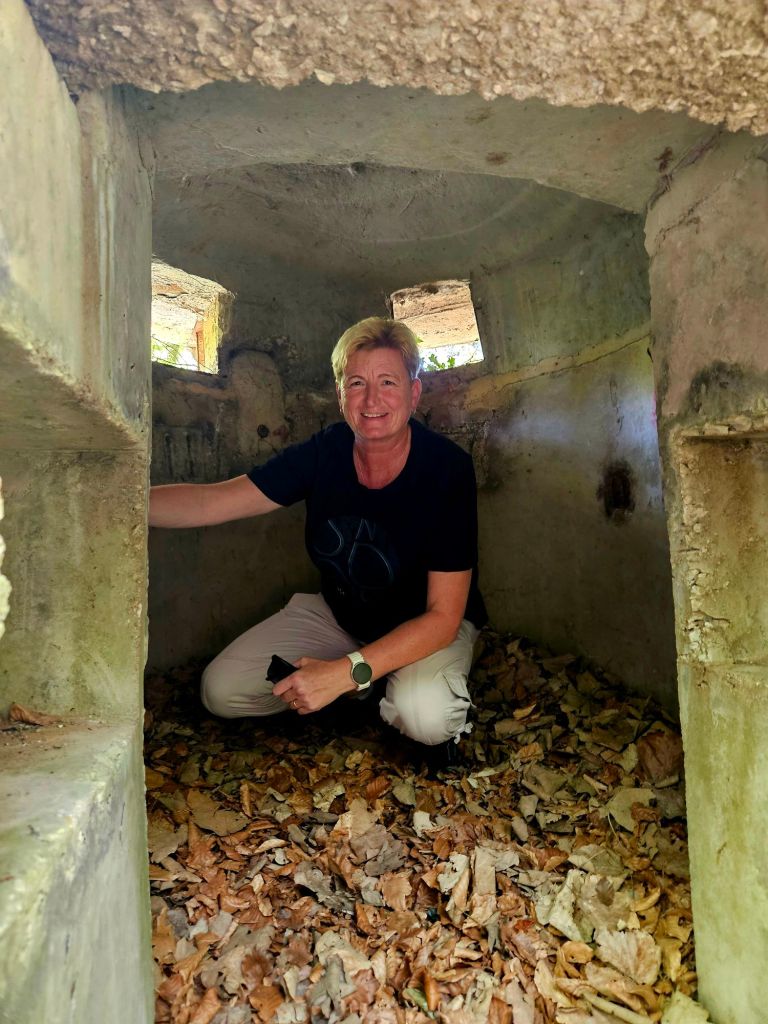




The weather was nice and the sun was shining so we walked around for a couple of hours.


We did see a black squirrel too. We tried to get a photo of it – it’s somewhere in the tree below!

And then we headed back to the cable car and headed back down.




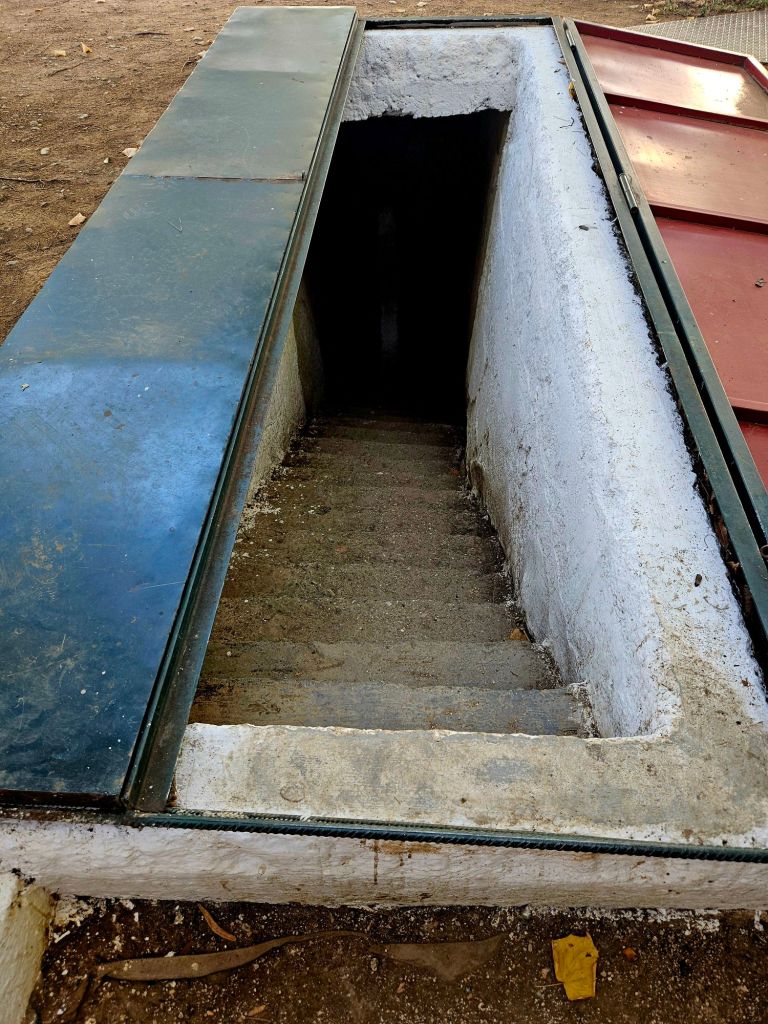
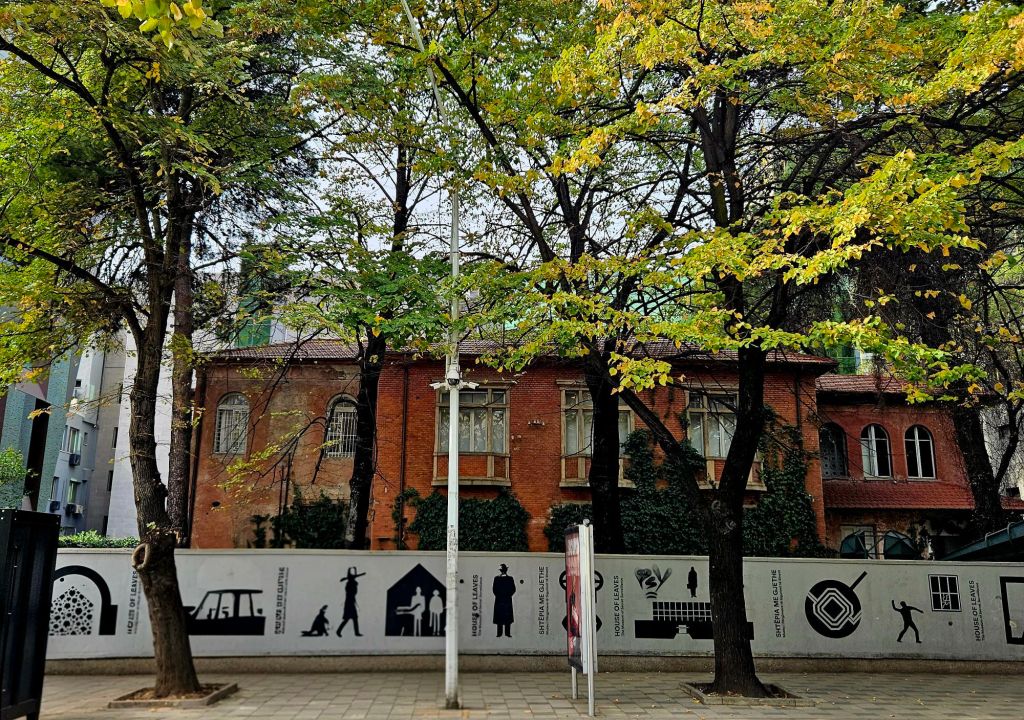
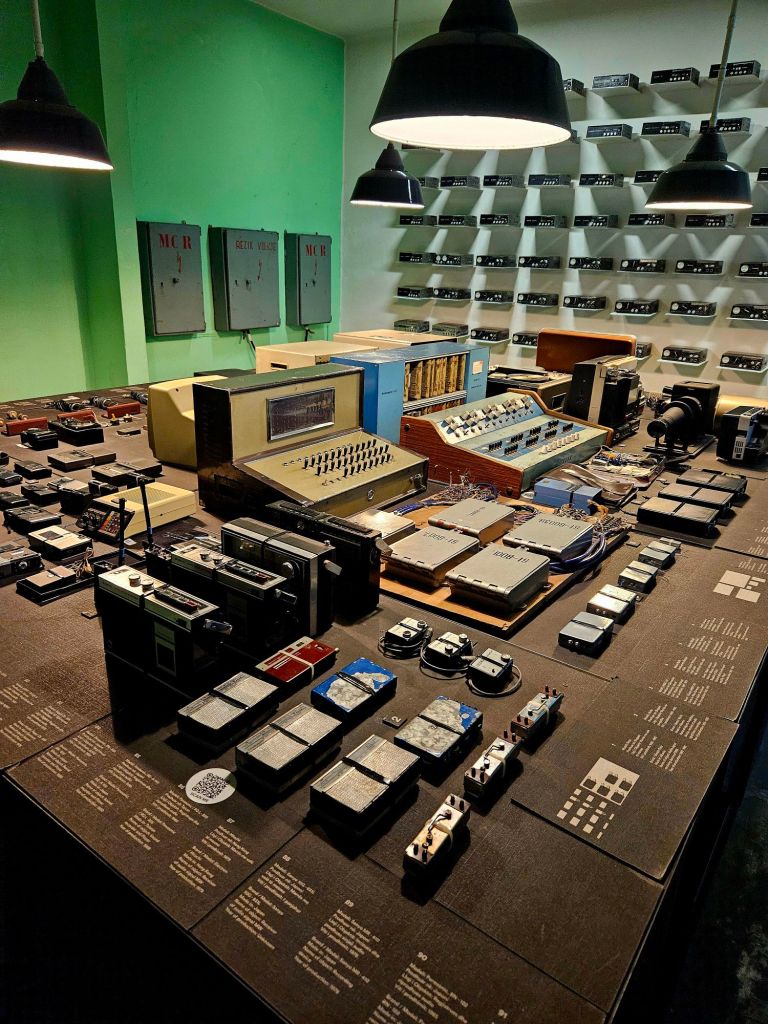
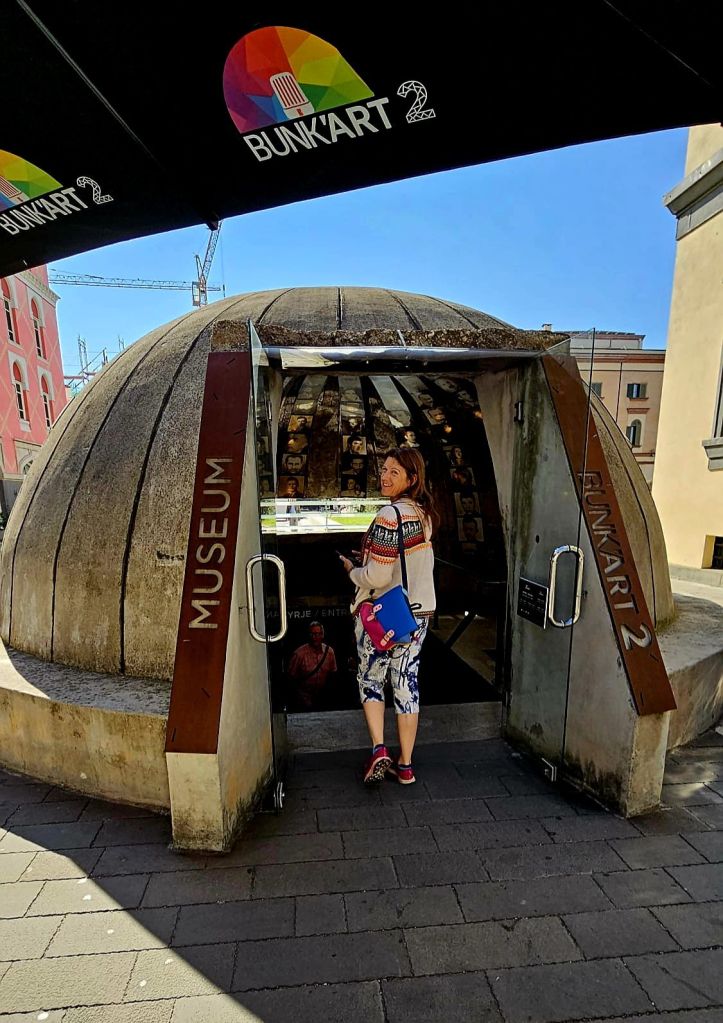
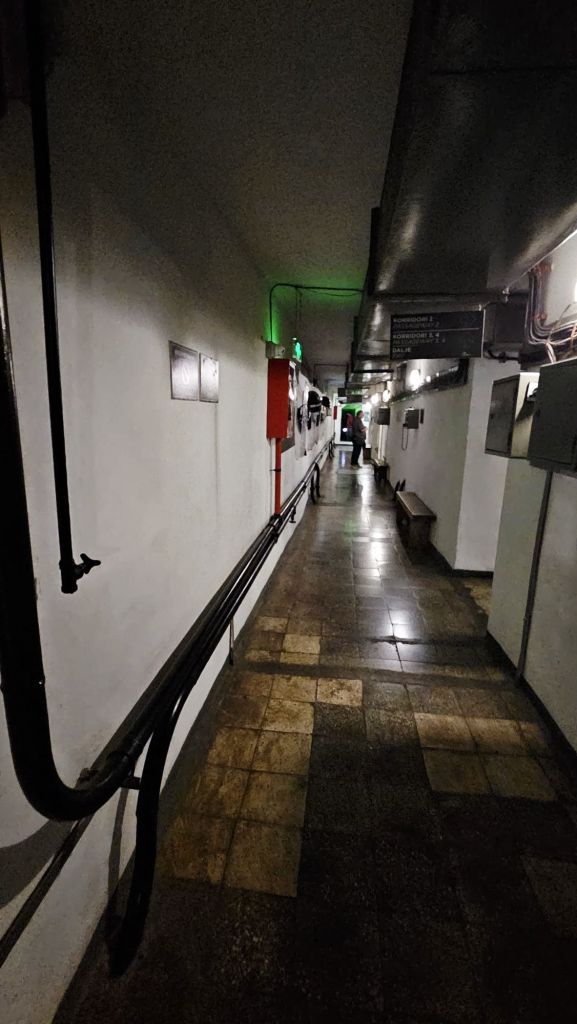
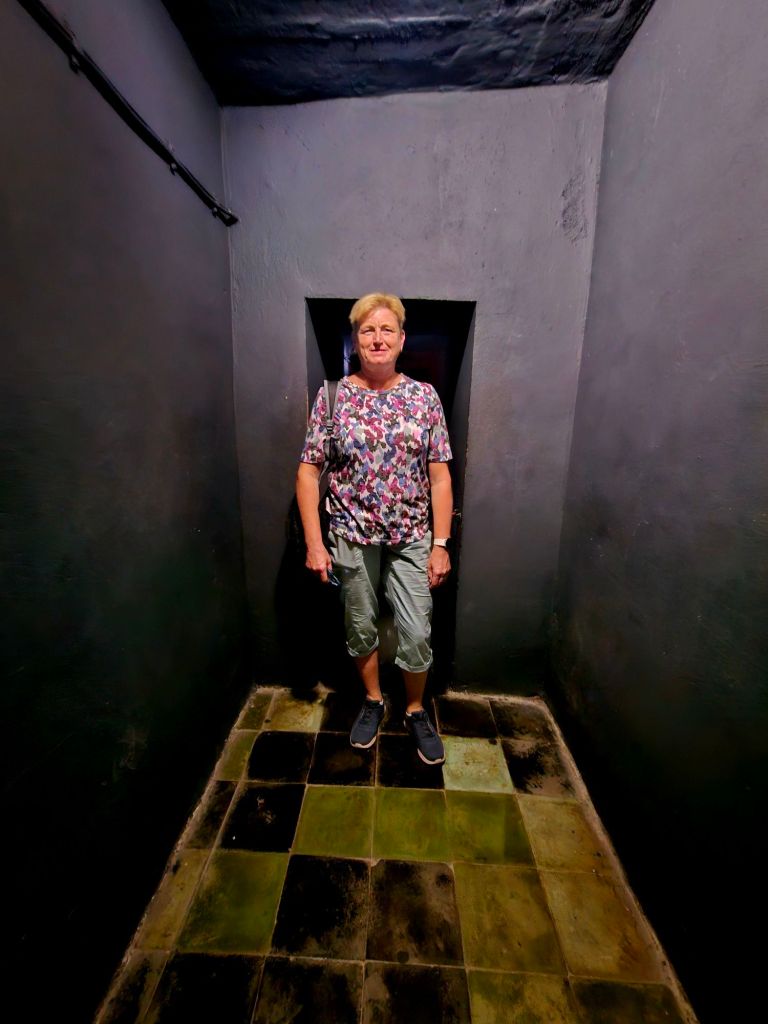
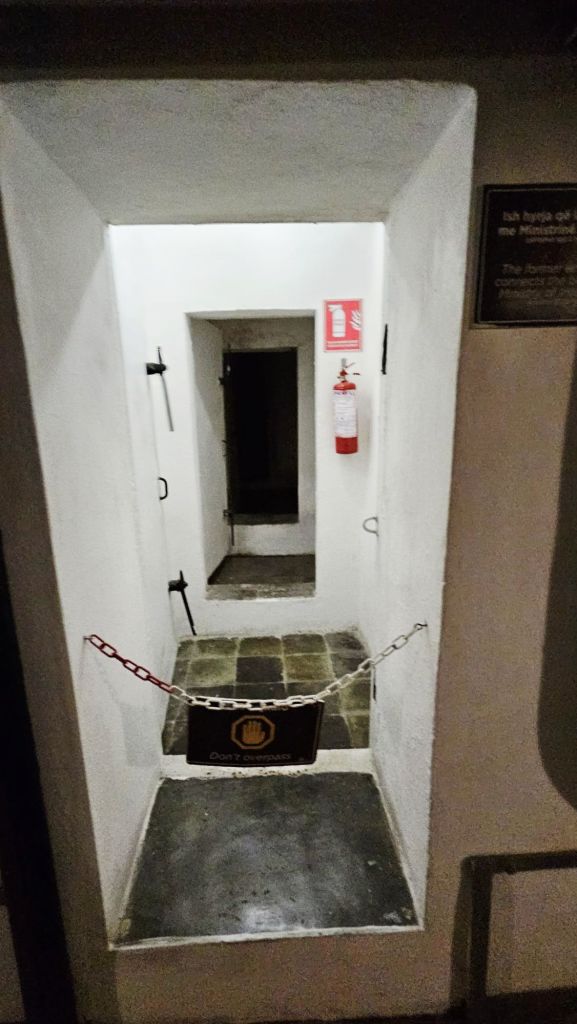
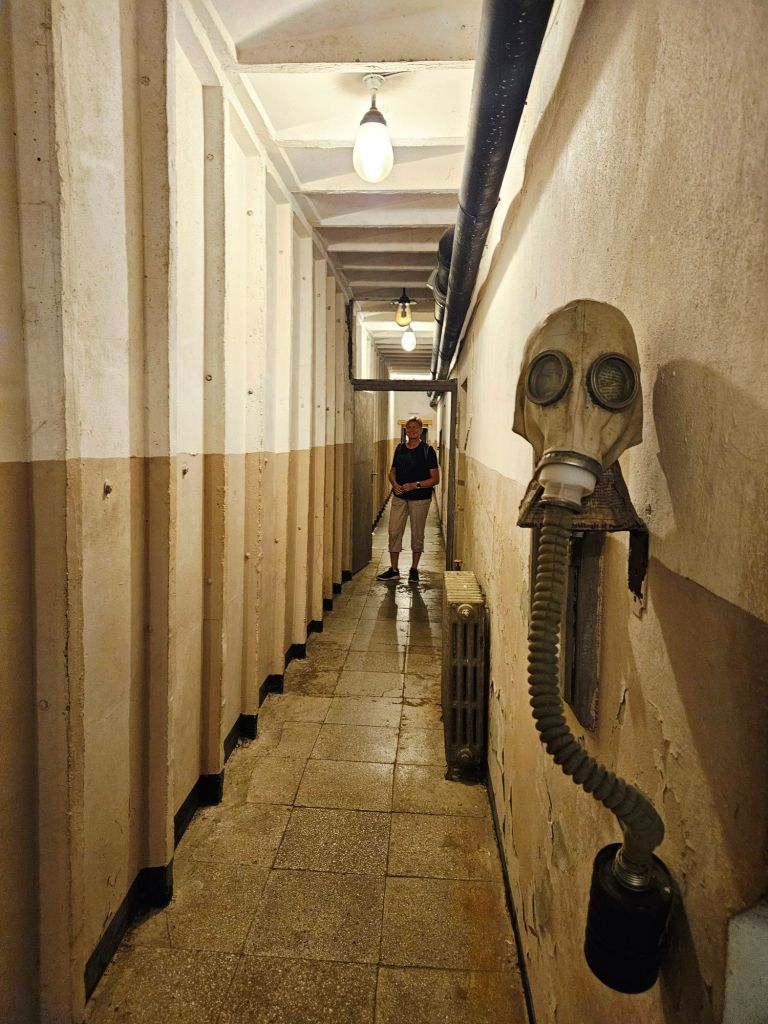
Quite close to where the cable car starts is Bunk’Art 1. This is a huge underground nuclear shelter and was built for Hoxha and the innermost circle of his government. It is built over 5 floors, contains 106 rooms and covers an area of 3000m². To get there you had to walk through a long dark tunnel.
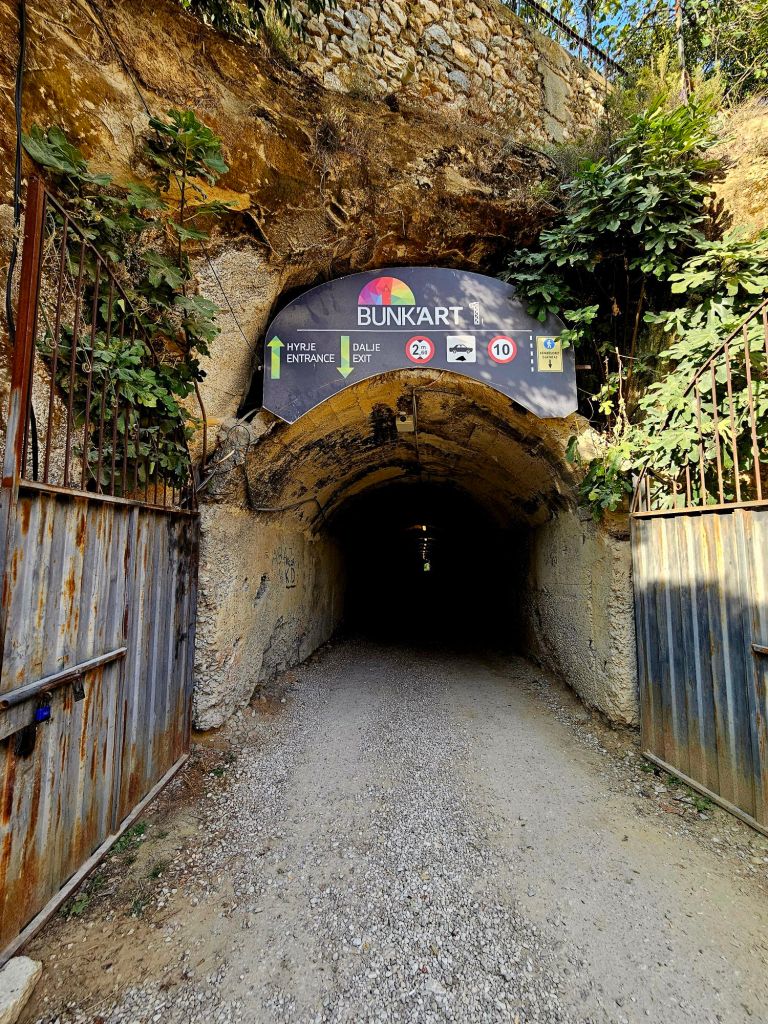

Between 2014 -2016 the bunker was refurbished and then opened as a museum dedicated to the history of the Albanian communist army and to the daily lives of Albanians during the regime. The bunker was built between 1972 -1978 and remained in military use until 1999.
At the end of the tunnel you buy your tickets and then walk through a wooded area, where you can already see parts of the bunker jutting out from the rock face. And eventually you get to the entrance.
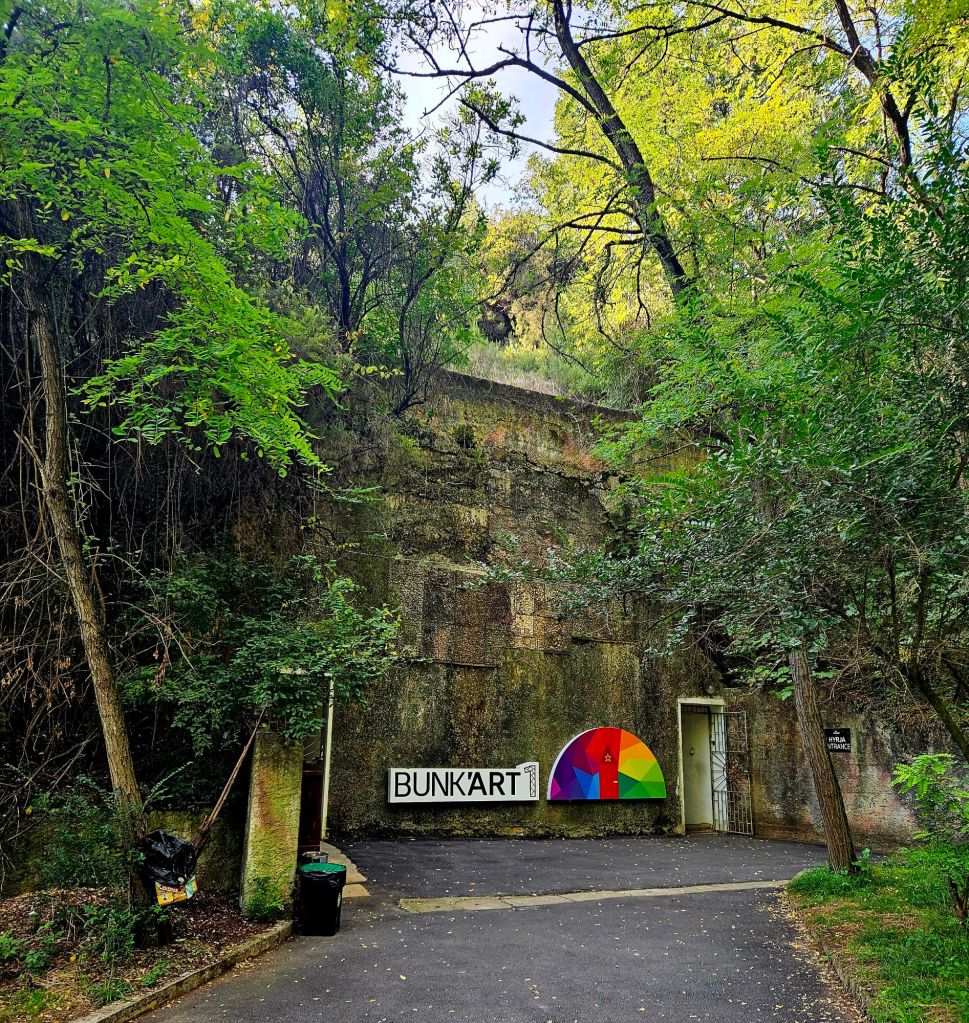

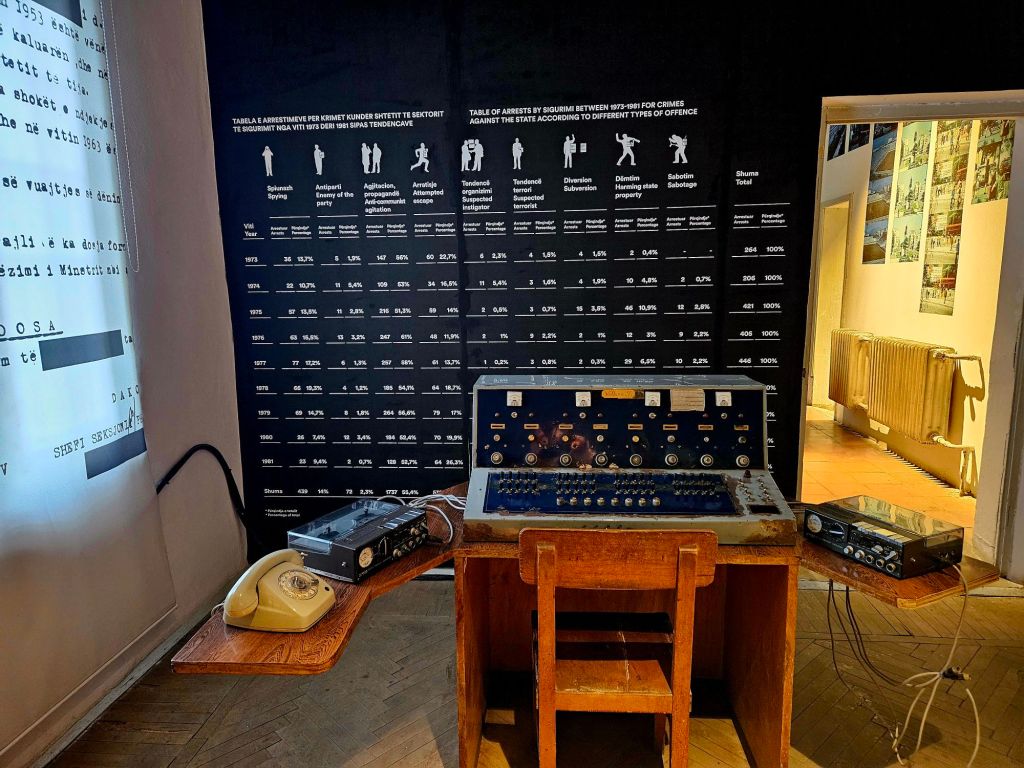
One of the first parts you come to is the private rooms for Enver Hoxha. On a small table there is a telephone and you can pick it up and listen to an audio recording of Hoxha.
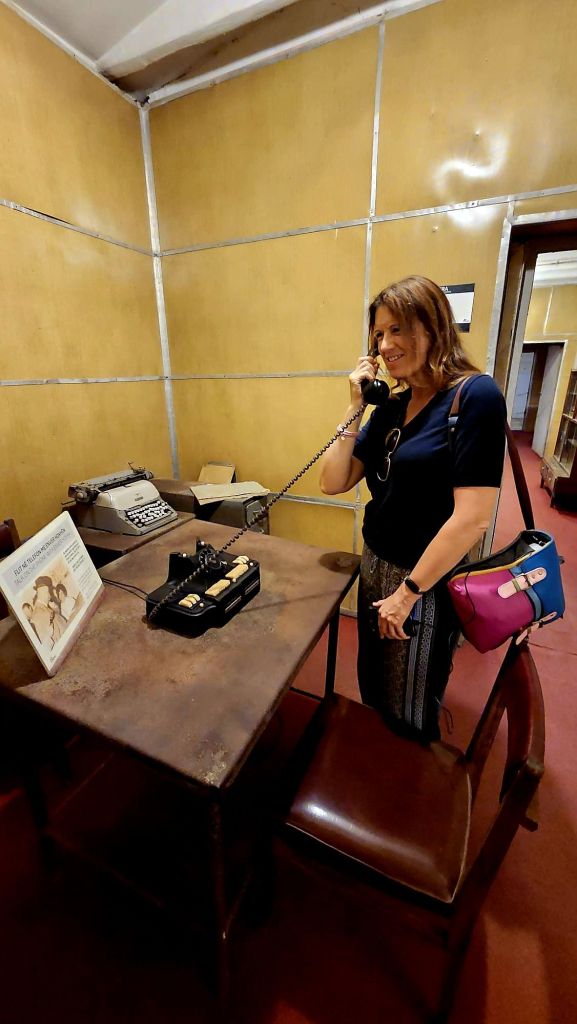

Although the rooms were definitely not five star luxury, they had carpets, specially veneered walls, comfortable armchairs and a seperate office. There is a double bed in the bedroom and a large bathroom with a shower, toilet and bidet.
Mehmet Shehu also had private quarters as part of this bunker complex. They are not quite as luxurious as those of Hoxha but also have a double bedroom, a living room and a bathroom.
We were not supposed to take photos, so I don’t have many from inside the bunker.
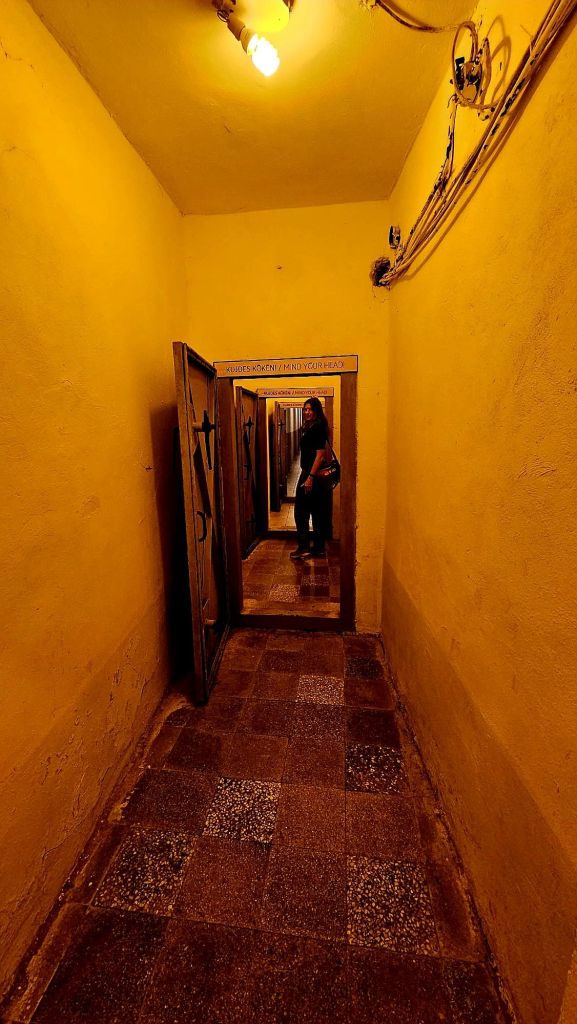

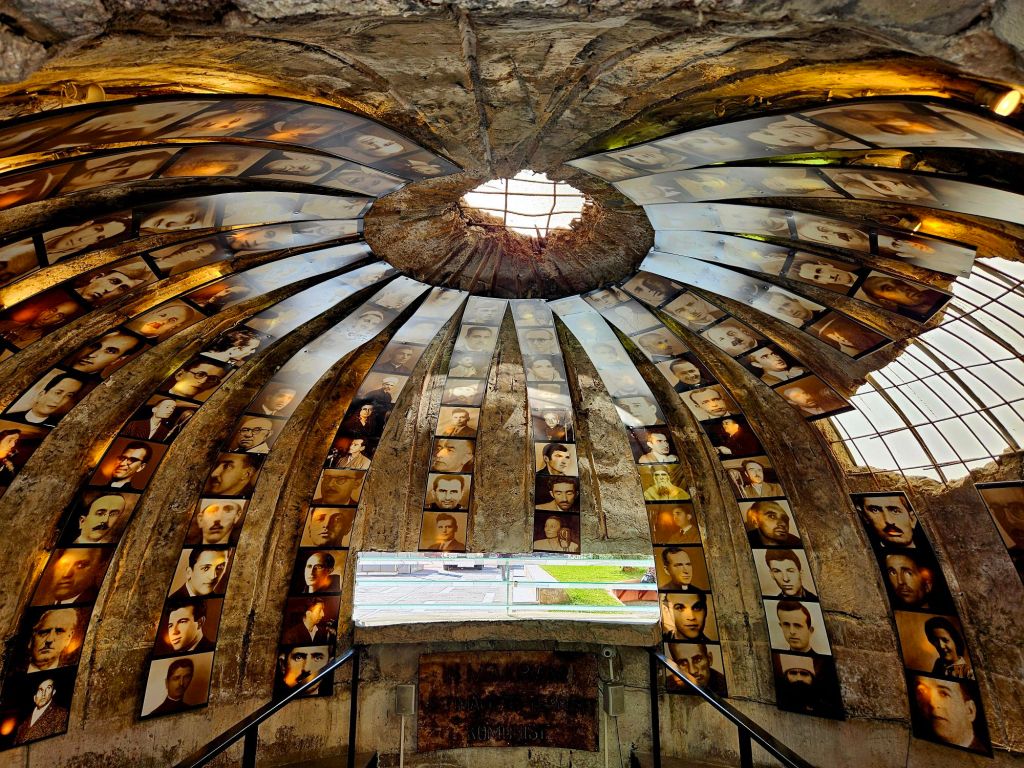
The historical exhibition starts with Italy’s facist occupation of Albania in WWII and then the Nazi German invasion a bit later in the war. It then moves on to the early phases of how Albania was shaped following its liberation and the efforts of the partisan army.
One room tells the story of the survivors of an American plane crash. The C53 plane was a transport plane and had to make an emergency landing on 8 November 1943. The 30 survivors were taken in by partisans, who also dismantled the plane and hid the parts. At the time the Americans were considered allies in the fight against the Germans. A man called Kostaq Stefa was tasked with leading the 30 survivors to freedom, through the mountains – a journey which lasted 63 days, one way. Once Hoxha was in power there was an anti-american sentiment. Kostaq was arrested in 1947 and tortured for 3 months and was sentenced to death in 1948. His wife appealed the sentence and it appeared that the sentence was reduced to life imprisonment. Eleni visited her husband for a brief 4 minutes and was told that he would be transferred to a state prison the next day. But he was killed by firing squad the next morning.
We passed one of the filter rooms. The air in the bunker is chemically filtered to ensure toxins do not get inside.
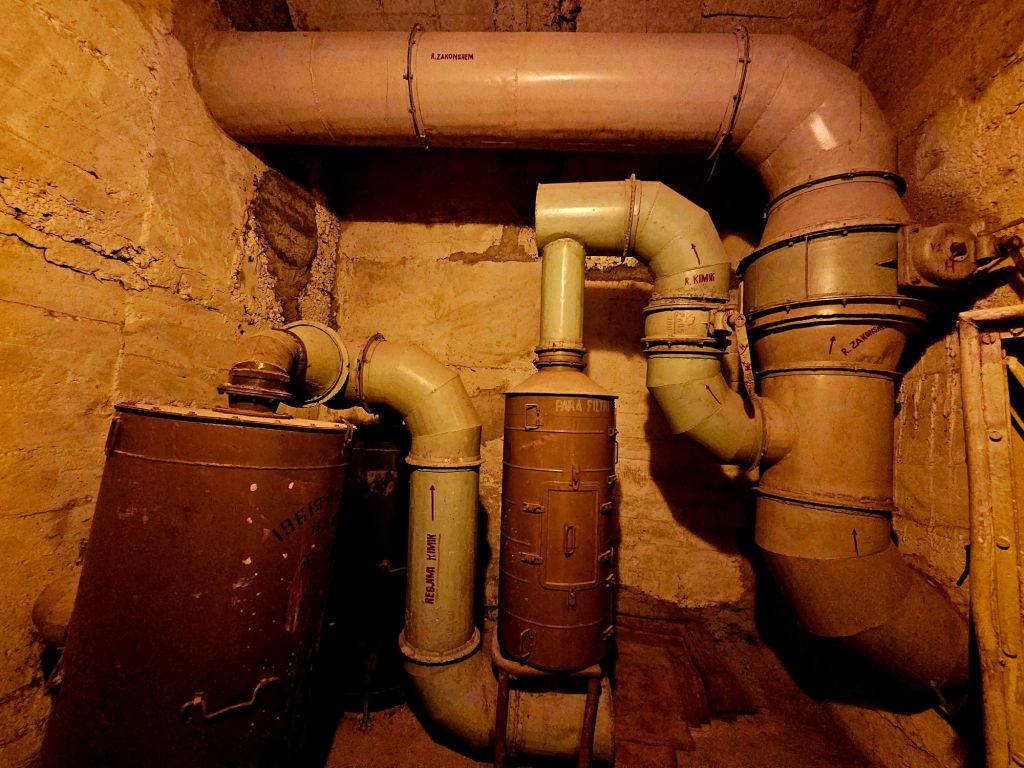

One room is all about chemical warfare as Hoxha was particularly paranoid about chemical weapons.

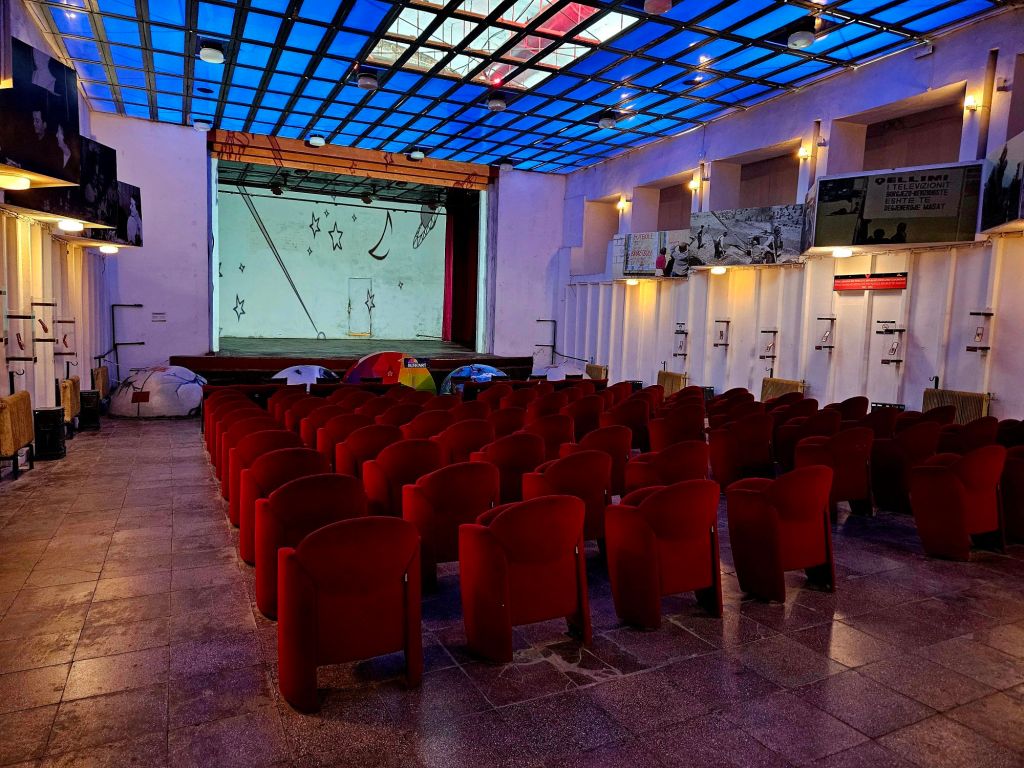
There is a huge assembly room in the bunker. This room is two storeys high, with a large stage and rows of theatre seats.

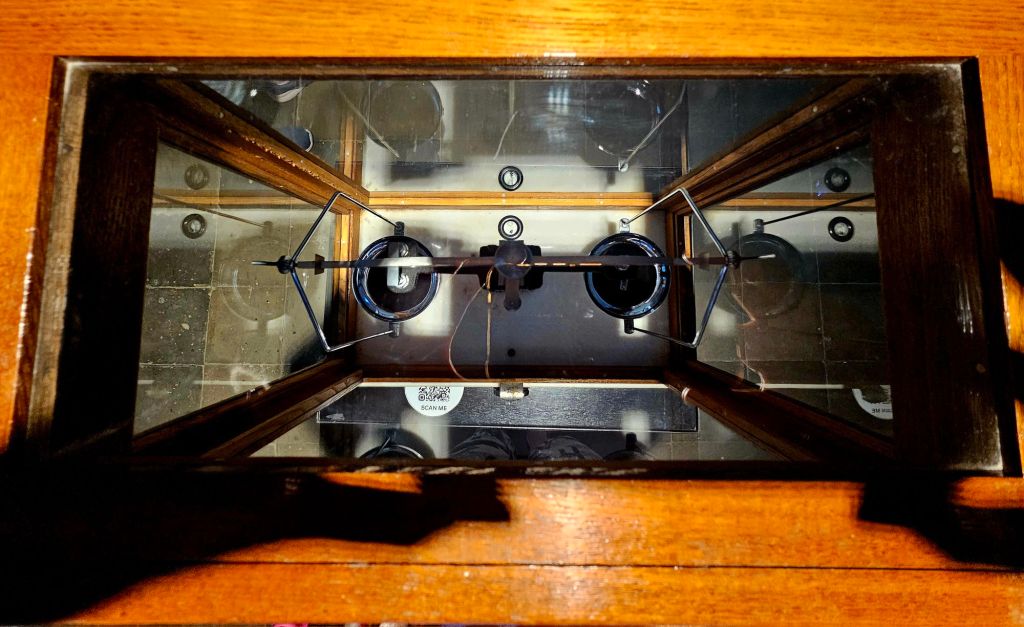
There are a couple of art exhibitions. One is a room of mirrors covered in war words.


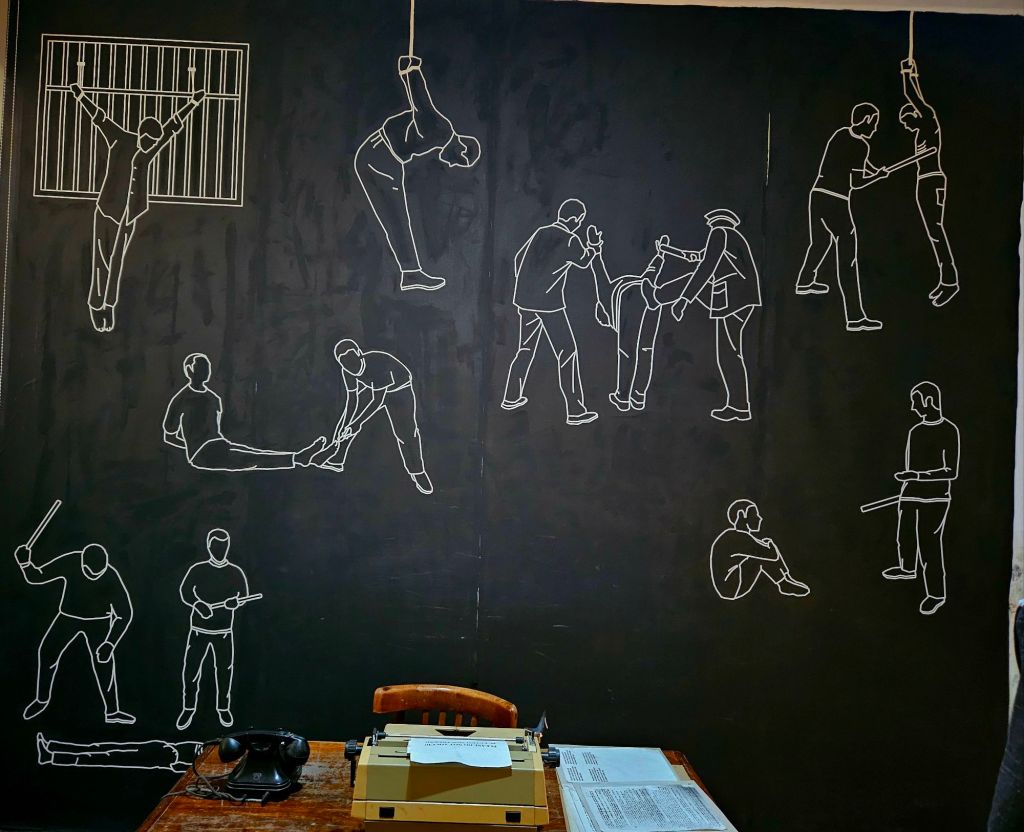
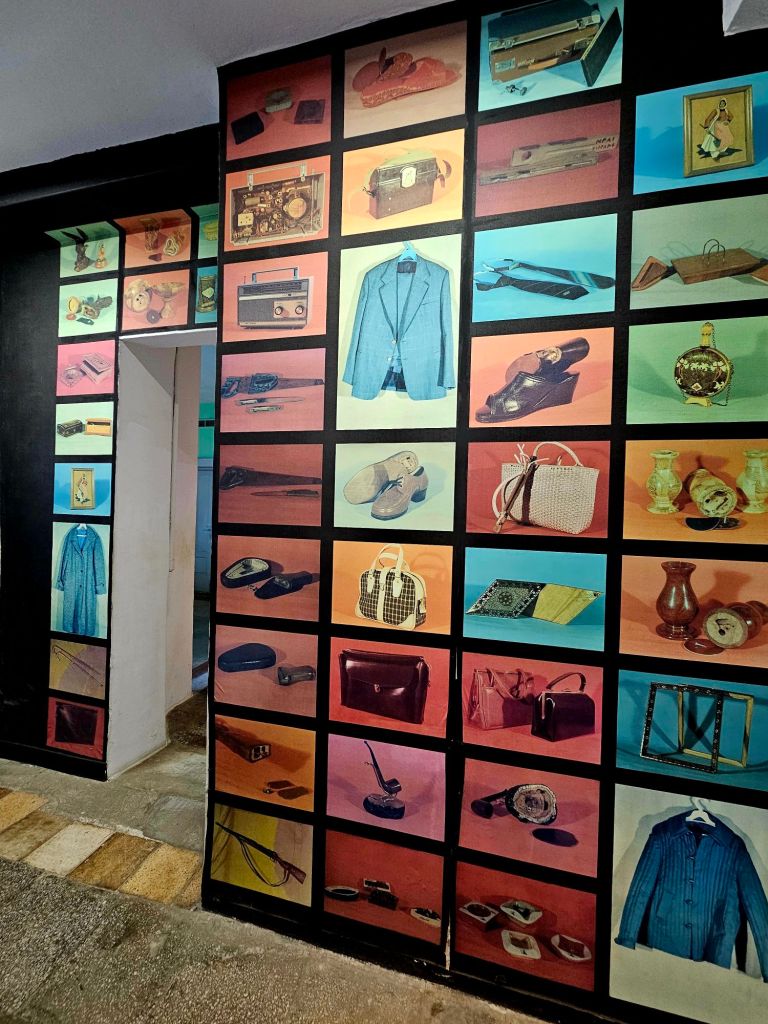
The everyday lives of Albanian citizens is reflected throughout the bunker and it highlights the fact they lived in constant fear. Many intellectuals were imprisoned, tortured or killed. Often their families also suffered the same fate.
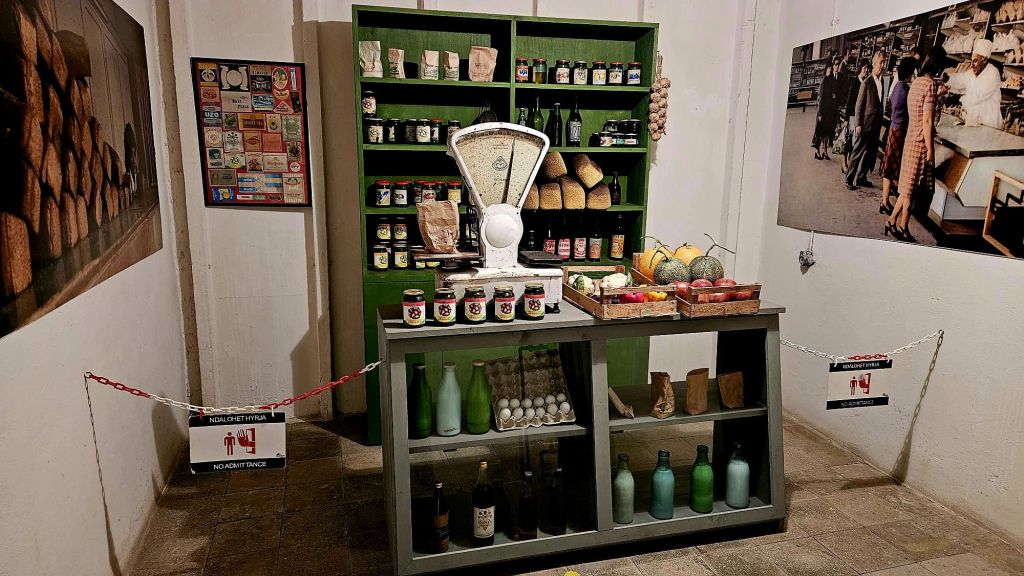
There is a replica of an grocery store as it would’ve been at the time.

The final exhibition room focuses on bats. Many of the former bunkers have become invaluable shelters for bats.
From the bunker we walked down to the bus stop – the long way round – and caught the bus back into Tirana centre. Some of the electrics and wiring we saw left a lot to be desired.
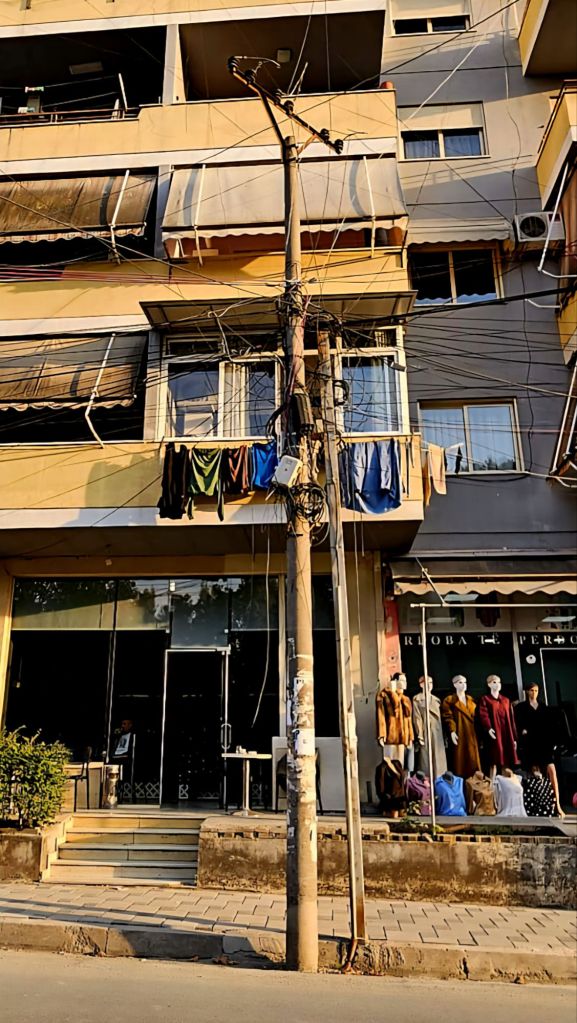

We went back to the apartment to change and freshen up. We couldn’t decide where to go for dinner so just wandered down one of the streets until we saw somewhere we both liked.

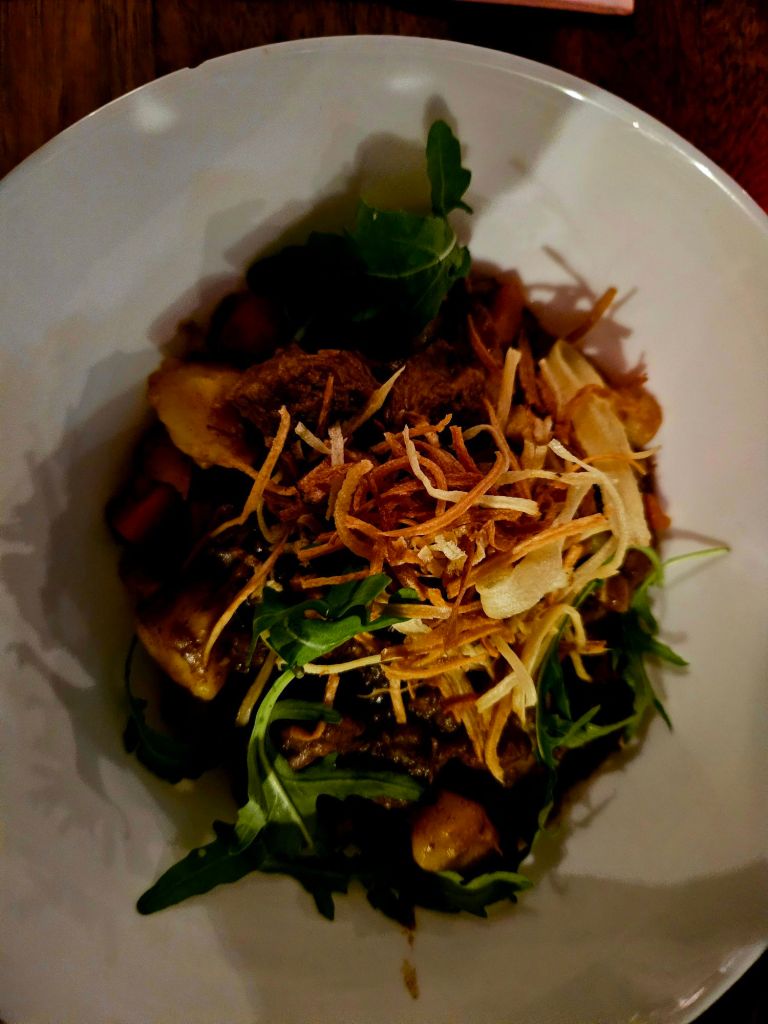
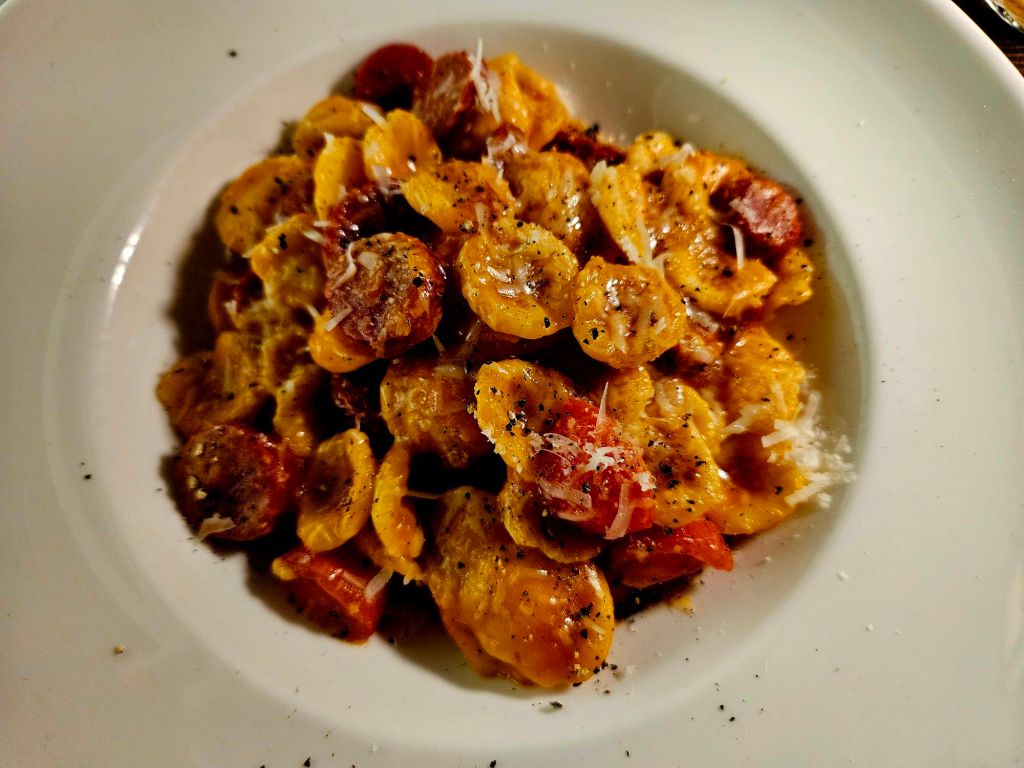
We ended up at Rooms restaurant. I had a beef pasta dish which was very tasty.

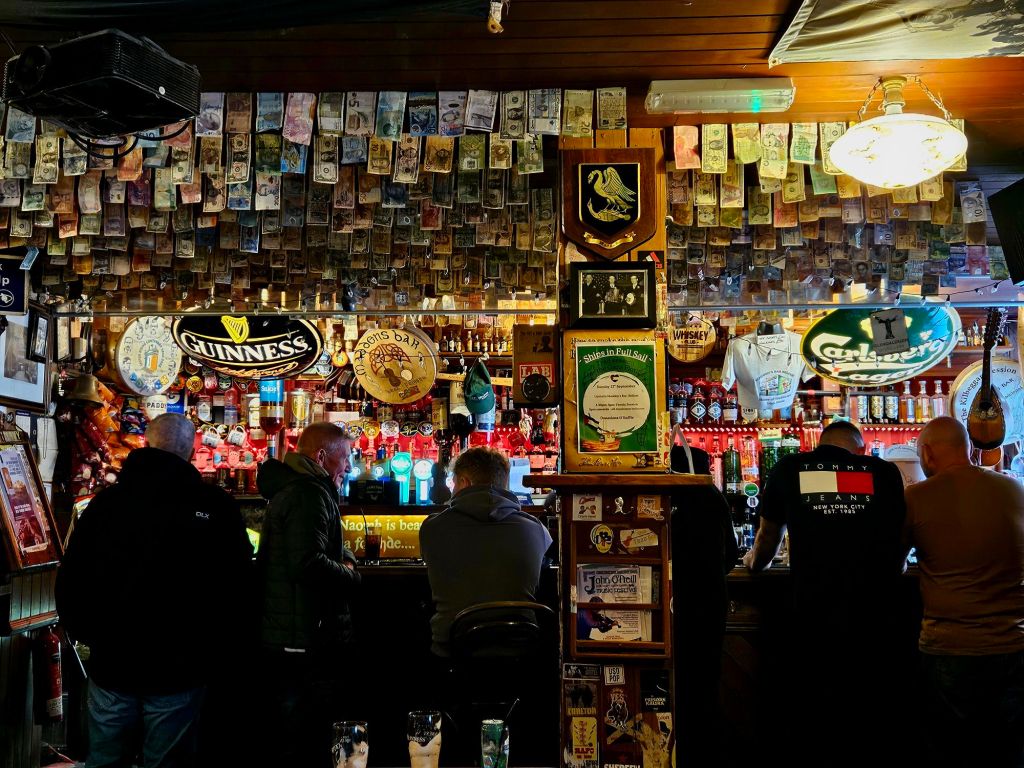
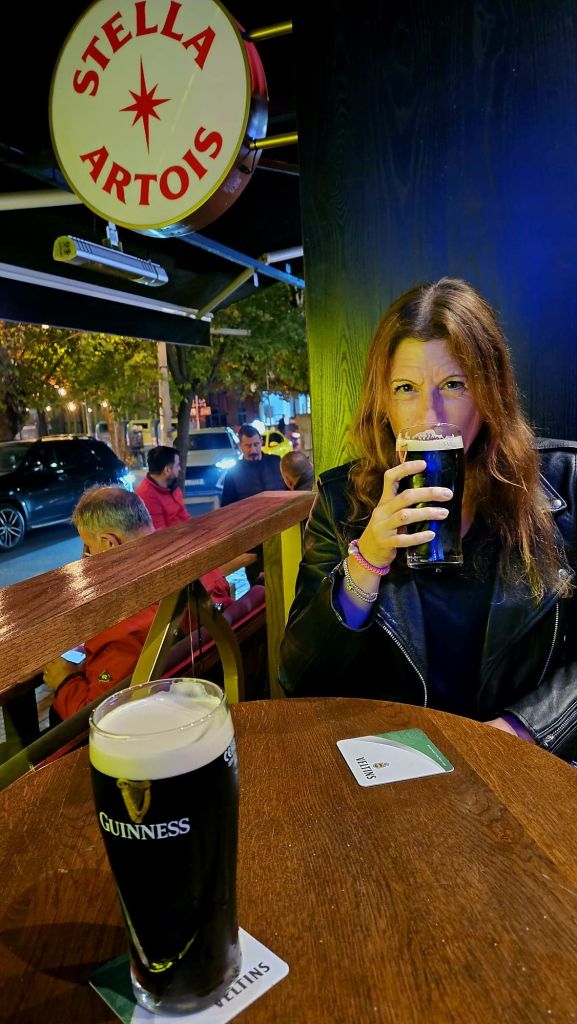
On the way back to the apartment we passed the Irish pub again, and this time they had Guiness. So obviously we had to stop for a pint.

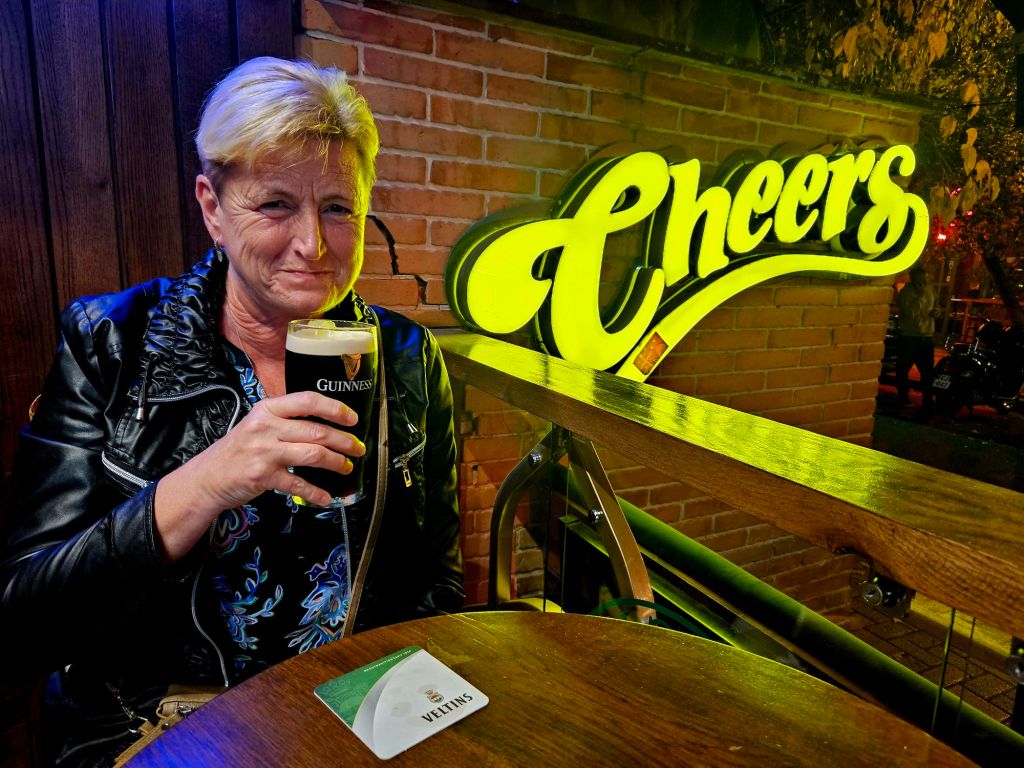
We then headed home to bed.